A pathway in quiescent cells that controls p27Kip1 stability, subcellular localization, and tumor suppression
- PMID: 16391232
- PMCID: PMC1356100
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1384406
A pathway in quiescent cells that controls p27Kip1 stability, subcellular localization, and tumor suppression
Abstract
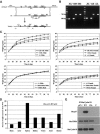
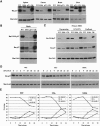
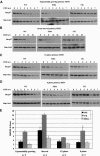
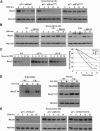
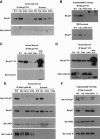
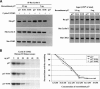
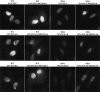
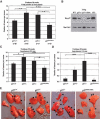
We have created two knock-in mouse models to study the mechanisms that regulate p27 in normal cells and cause misregulation of p27 in tumors: p27(S10A), in which Ser10 is mutated to Ala; and p27(CK-), in which point mutations abrogate the ability of p27 to bind cyclins and CDKs. These two mutant alleles identify steps in a pathway that controls the proteasomal degradation of p27 uniquely in quiescent cells: Dephosphorylation of p27 on Ser10 inhibits p27 nuclear export and promotes its assembly into cyclin-CDK complexes, which is, in turn, necessary for p27 turnover. We further show that Ras-dependent lung tumorigenesis is associated with increased phosphorylation on Ser10 and cytoplasmic mislocalization of p27. Indeed, we find that p27(S10A) is refractory to Ras-induced cytoplasmic translocation and that p27(S10A) mice are tumor resistant. Thus, phosphorylation of p27 on Ser10 is an important event in the regulation of the tumor suppressor function of p27.
Figures
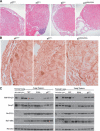
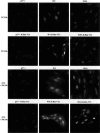
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
