Anthrax lethal factor protease inhibitors: synthesis, SAR, and structure-based 3D QSAR studies
- PMID: 16392787
- PMCID: PMC3164827
- DOI: 10.1021/jm050892j
Anthrax lethal factor protease inhibitors: synthesis, SAR, and structure-based 3D QSAR studies
Abstract
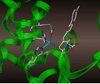
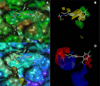
We have recently identified a series of compounds that efficiently inhibit anthrax lethal factor (LF) metallo-protease. Here we present further structure-activity relationship and CoMFA (comparative molecular field analysis) studies on newly derived inhibitors. The obtained 3D QSAR model was subsequently compared with the X-ray structure of the complex between LF and a representative compound. Our studies form the basis for the rational design of additional compounds with improved activity and selectivity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Guanidinylated 2,5-dideoxystreptamine derivatives as anthrax lethal factor inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Mar 15;16(6):1527-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.12.038. Epub 2006 Jan 4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006. PMID: 16386899
-
QSAR and molecular docking studies of lethal factor protease inhibitors against Bacillus anthracis.SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2019 Oct;30(10):715-731. doi: 10.1080/1062936X.2019.1658219. Epub 2019 Sep 26. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2019. PMID: 31556709
-
Rhodanine derivatives as selective protease inhibitors against bacterial toxins.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008 Feb;71(2):131-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2007.00617.x. Epub 2008 Jan 19. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008. PMID: 18221310
-
Discovery and development of anthrax lethal factor metalloproteinase inhibitors.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2008 Feb;9(1):24-33. doi: 10.2174/138920108783497604. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18289054 Review.
-
Quickening the pace of anthrax research: three advances point towards possible therapies.Trends Microbiol. 2002 Feb;10(2):58-62. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(01)02294-6. Trends Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11827799 Review.
Cited by
-
Chelator fragment libraries for targeting metalloproteinases.ChemMedChem. 2010 Feb 1;5(2):195-9. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900516. ChemMedChem. 2010. PMID: 20058293 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic polyamines inhibit anthrax lethal factor protease.BMC Pharmacol. 2006 Jun 8;6:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-6-8. BMC Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16762077 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput screening approach to anthrax lethal factor inhibition.Bioorg Chem. 2007 Aug;35(4):306-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2006.12.005. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Bioorg Chem. 2007. PMID: 17320146 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel non-hydroxamate anthrax toxin lethal factor inhibitors by topomeric searching, docking and scoring, and in vitro screening.J Chem Inf Model. 2009 Dec;49(12):2726-34. doi: 10.1021/ci900186w. J Chem Inf Model. 2009. PMID: 19928768 Free PMC article.
-
3-Phenyl-2-thioxo-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008 Sep 24;64(Pt 10):o1998. doi: 10.1107/S1600536808030079. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008. PMID: 21201196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith H, Keppie J. Observations on experimental anthrax: demonstration of a specific lethal factor produced in vivo by Bacillus anthracis. Nature. 1954;173:869–870. - PubMed
-
- Hanna P. Anthrax pathogenesis and host response. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 1998;225:13–35. - PubMed
-
- Stubbs MT. Anthrax X-rayed: new opportunities for bio-defense. TRENDS Pharmacol Sci. 2002;23:539–541. - PubMed
-
- Bradley KA, Mogridge J, Mourez M, Collier RJ, Young JA. Identification of the cellular receptor for anthrax toxin. Nature. 2001;414:225–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

