Surface clustering of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 induced by long Homer proteins
- PMID: 16393337
- PMCID: PMC1361788
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-1
Surface clustering of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 induced by long Homer proteins
Abstract
Background: Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) regulate neuronal excitability and synaptic strength. The group I mGluRs, mGluR1 and 5, are widespread in the brain and localize to post-synaptic sites. The Homer protein family regulates group I mGluR function and distribution. Constitutively expressed 'long' Homer proteins (Homer 1b, 1c, 2 and 3) induce dendritic localization of group I mGluRs and receptor clustering, either internally or on the plasma membrane. Short Homer proteins (Homer 1a, Ania-3) exhibit regulated expression and act as dominant negatives, producing effects on mGluR distribution and function that oppose those of the long Homer proteins. There remains some controversy over whether long Homer proteins induce receptor internalization by inducing retention in the endoplasmic reticulum, or induce mGluR clustering on the plasma membrane. Further, an exhaustive study of the effects of each long Homer isoform on mGluR distribution has not been published.
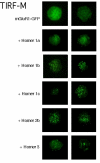
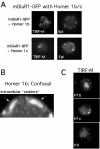
Results: The distribution of a GFP-tagged group I mGluR, mGluR1-GFP, was examined in the absence of Homer proteins and in the presence of several Homer isoforms expressed in sympathetic neurons from the rat superior cervical ganglion (SCG) using total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF-M) and confocal microscopy. Quantitative analysis of mGluR1-GFP fluorescence using TIRF-M revealed that expression of each long Homer isoform tested (Homer 1b, 1c, 2b and 3) induced a significant degree of surface clustering. Using confocal imaging, Homer-induced mGluR clusters were observed intra-cellularly as well as on the plasma membrane. Further, in approximately 40% of neurons co-expressing mGluR1-GFP and Homer 1b, intracellular inclusions were observed, but plasma membrane clusters were also documented in some Homer 1b coexpressing cells.
Conclusion: All long Homer proteins examined (Homer 1b, 1c, 2b and 3) induced a significant degree of mGluR1-GFP clustering on the plasma membrane compared to cells expressing mGluR1-GFP alone. Clusters induced by long Homers appeared on the plasma membrane and intracellularly, suggesting that clusters form prior to plasma membrane insertion and/or persist after internalization. Finally, while Homer 1b induced surface clustering of mGluR1 in some cells, under some conditions intracellular retention may occur.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Homer proteins regulate coupling of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors to N-type calcium and M-type potassium channels.J Neurosci. 2000 Oct 1;20(19):7238-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07238.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11007880 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous homer proteins regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling in neurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Aug 20;28(34):8560-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1830-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18716215 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5-green fluorescent protein chimera (mGluR5-GFP): pharmacology, surface expression, and differential effects of Homer-1a and Homer-1c.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001 Sep;18(3):296-306. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2001.1031. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11591130
-
Homer/Vesl proteins and their roles in CNS neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Jun;29(3):213-27. doi: 10.1385/MN:29:3:213. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15181235 Review.
-
Distinct physiological roles of the Gq-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors Co-expressed in the same neuronal populations.J Cell Physiol. 2002 May;191(2):125-37. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10081. J Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12064455 Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamate system, amyloid ß peptides and tau protein: functional interrelationships and relevance to Alzheimer disease pathology.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013 Jan;38(1):6-23. doi: 10.1503/jpn.110190. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22894822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated postsynaptic density and endocytic zone in the amygdala of human heroin and cocaine abusers.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Feb 1;69(3):245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.037. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21126734 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mGluR5 neurotransmission in reinstated cocaine-seeking.Addict Biol. 2013 Jan;18(1):40-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00432.x. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Addict Biol. 2013. PMID: 22340009 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Trafficking and its Role in Drug-Induced Neurobehavioral Plasticity.Brain Plast. 2021 Oct 19;7(2):61-76. doi: 10.3233/BPL-210120. eCollection 2021. Brain Plast. 2021. PMID: 34868874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential gene expression in the nucleus accumbens with ethanol self-administration in inbred alcohol-preferring rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Jun;89(4):481-98. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.01.023. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008. PMID: 18405950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schoepp DD. Unveiling the functions of presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;299:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Huber KM, Roder JC, Bear MF. Chemical induction of mGluR5- and protein synthesis--dependent long- term depression in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:321–325. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

