Reproductive disruption in wild longear sunfish (Lepomis megalotis) exposed to kraft mill effluent
- PMID: 16393656
- PMCID: PMC1332654
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.8130
Reproductive disruption in wild longear sunfish (Lepomis megalotis) exposed to kraft mill effluent
Abstract
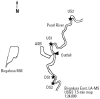
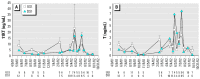
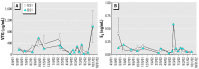
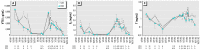
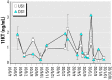
Worldwide, wild fish living in rivers receiving municipal and industrial discharges may experience endocrine disruption as a result of exposure to anthropogenic pollutants. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the hormonal status of wild fish in a U.S. river receiving unbleached kraft and recycled pulp mill effluent (Pearl River at Bogalusa, LA). We evaluated two alternative hypotheses: the effluent contained constituents that suppressed male and female reproduction, or it contained an androgenic substance that masculinized females. To evaluate the likelihood of fish exposure to effluent, we marked 697 longear sunfish (Lepomis megalotis) over a 2-year period; 83% of recaptured fish were found at the site of initial capture, and only one fish migrated from an effluent-receiving site to a reference site. We can reasonably assume that fish captured from an effluent-receiving site are residents, not transitory migrants. To diagnose endocrine disruption, we measured sex steroid hormone [17beta-estradiol (E2), testosterone (T), and 11-ketotestosterone (11KT)] and vitellogenin (VTG) concentrations in male and female longear sunfish captured at two sites upstream and two sites downstream of the effluent outfall. Kraft pulp mill effluent did not affect male reproductive physiology but did suppress female T and VTG levels when effluent constituted>or=1% of river flow. Masculinization was not observed. Longear sunfish in the Pearl River experience moderate reproductive suppression in response to unbleached kraft and recycled pulp mill effluent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of pulp and paper mill effluents on reproductive success of largemouth bass.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003 Jan;22(1):205-13. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12503766
-
Assessment of reproductive effects in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to bleached/unbleached kraft mill effluents.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2001 Nov;41(4):475-82. doi: 10.1007/s002440010274. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11598785
-
Investigating the link between pulp mill effluent and endocrine disruption: attempts to explain the presence of intersex fish in the Wabigoon River, Ontario, Canada.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2010 Apr;29(4):952-65. doi: 10.1002/etc.118. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20821526
-
A decade of research on the environmental impacts of pulp and paper mill effluents in Canada: development and application of fish bioassays.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2006 Jul-Aug;9(4):297-317. doi: 10.1080/15287390500195752. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2006. PMID: 16723329 Review.
-
Altered reproduction in fish exposed to pulp and paper mill effluents: roles of individual compounds and mill operating conditions.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008 Mar;27(3):682-97. doi: 10.1897/07-195.1. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008. PMID: 17973561 Review.
Cited by
-
The Bioaccumulation and Biodegradation of Testosterone by Chlorella vulgaris.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Apr 8;16(7):1253. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071253. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30965641 Free PMC article.
-
Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana.Toxics. 2024 Mar 30;12(4):259. doi: 10.3390/toxics12040259. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38668483 Free PMC article.
-
Toward sustainable environmental quality: Identifying priority research questions for Latin America.Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2018 May;14(3):344-357. doi: 10.1002/ieam.2023. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2018. PMID: 29469193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams S, Ham K, Greeley M, LeHew R, Hinton D, Saylor C. Downstream gradients in bioindicator responses: point source contaminant effects on fish health. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 1996;53:2177–2187.
-
- Berra T, Gunning G. Seasonal movement and home range of the longear sunfish, Lepomis megalotis (Rafinesque) in Louisiana. Am Midl Nat. 1972;88:368–375.
-
- Bortone S, Davis W. Fish intersexuality as indicator of environmental stress. Bioscience. 1994;44:165–172.
-
- Bouma J, Nagler J. Estrogen receptor-α protein localization in the testis of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during different stages of the reproductive cycle. Biol Reprod. 2001;65:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Brantley RK, Wingfield JC, Bass AH. Sex steroid levels in Porichthys notatus, a fish with alternative reproductive tactics, and a review of the hormonal bases for male dimorphism among teleost fishes. Horm Behav. 1993;27:332–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

