Early growth response-1 is required for CD154 transcription
- PMID: 16393964
- PMCID: PMC1424665
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.2.811
Early growth response-1 is required for CD154 transcription
Abstract
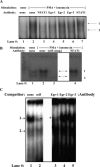
CD154 (CD40 ligand) expression on CD4 T cells is normally tightly controlled, but abnormal or dysregulated expression of CD154 has been well documented in autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus. Beyond regulation by NFAT proteins, little is known about the transcriptional activation of the CD154 promoter. We identified a species-conserved purine-rich sequence located adjacent to the CD154 transcriptional promoter proximal NFAT site, which binds early growth response (Egr) transcription factors. Gel shift assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays reveal that Egr-1, Egr-3, and NFAT1 present in primary human CD4 T cells are capable of binding this combinatorial site in vitro and in vivo, respectively. Multimerization of this NFAT/Egr sequence in the context of a reporter gene demonstrates this sequence is transcriptionally active upon T cell activation in primary human CD4 T cells. Overexpression of Egr-1, but not Egr-3, is capable of augmenting transcription of this reporter gene as well as that of an intact CD154 promoter. Conversely, overexpression of small interfering RNA specific for Egr-1 in primary human CD4 T cells inhibits CD154 expression. Similarly, upon activation, CD154 message is notably decreased in splenic CD4 T cells from Egr-1-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls. Our data demonstrate that Egr-1 is required for CD154 transcription in primary CD4 T cells. This has implications for selective targeting of Egr family members to control abnormal expression of CD154 in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures





Similar articles
-
IL-15 prolongs CD154 expression on human CD4 T cells via STAT5 binding to the CD154 transcriptional promoter.Genes Immun. 2014 Apr-May;15(3):137-44. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.3. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Genes Immun. 2014. PMID: 24500400 Free PMC article.
-
A T-cell-specific CD154 transcriptional enhancer located just upstream of the promoter.Genes Immun. 2008 Oct;9(7):640-9. doi: 10.1038/gene.2008.67. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Genes Immun. 2008. PMID: 18719603 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged expression of CD154 on CD4 T cells from pediatric lupus patients correlates with increased CD154 transcription, increased nuclear factor of activated T cell activity, and glomerulonephritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Aug;62(8):2499-509. doi: 10.1002/art.27554. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20506525 Free PMC article.
-
CD154 transcriptional regulation in primary human CD4 T cells.Immunol Res. 2003;27(2-3):185-202. doi: 10.1385/IR:27:2-3:185. Immunol Res. 2003. PMID: 12857968 Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in lymphocytes: the case of CD154.RNA Biol. 2009 Jul-Aug;6(3):259-65. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.3.8581. Epub 2009 Jul 29. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19395873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-15 prolongs CD154 expression on human CD4 T cells via STAT5 binding to the CD154 transcriptional promoter.Genes Immun. 2014 Apr-May;15(3):137-44. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.3. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Genes Immun. 2014. PMID: 24500400 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted regulatory mechanisms of the EGR family in tumours and prospects for therapeutic applications (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jul;56(1):113. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5554. Epub 2025 May 30. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40444475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGR-2 is not required for in vivo CD4 T cell mediated immune responses.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 23;5(9):e12904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012904. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20886122 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response-1 (EGR-1) and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) cooperate to mediate CD40L expression in megakaryocytes and platelets.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 22;288(47):33985-33996. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511881. Epub 2013 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24106272 Free PMC article.
-
FOXP3 inhibits activation-induced NFAT2 expression in T cells thereby limiting effector cytokine expression.J Immunol. 2009 Jul 15;183(2):907-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0800216. Epub 2009 Jun 29. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19564342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banchereau J, Bazan F, Blanchard D, Briere F, Galizzi JP, van Kooten C, Liu YJ, Rousset F, Saeland S. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. - PubMed
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2000;67:2–17. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Flavell RA. The CD40 ligand: at the center of the immune universe? Immunol. Res. 1997;16:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell-mediated immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:111–135. - PubMed
-
- Cron RQ. CD154 and lupus. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2003;1:172–181.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30-HH2815/HH/HHS/United States
- T32-AI007621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI35513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR48257/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AR49335/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR049335/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR240/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AI054233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI42185/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048257/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI054233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000240/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

