KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for CUL3-dependent ubiquitin ligase that regulates synaptic glutamate receptor turnover
- PMID: 16394099
- PMCID: PMC1382314
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0794
KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for CUL3-dependent ubiquitin ligase that regulates synaptic glutamate receptor turnover
Abstract
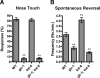
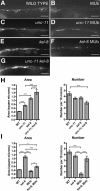
The regulated localization of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) to synapses is an important component of synaptic signaling and plasticity. Regulated ubiquitination and endocytosis determine the synaptic levels of AMPARs, but it is unclear which factors conduct these processes. To identify genes that regulate AMPAR synaptic abundance, we screened for mutants that accumulate high synaptic levels of the AMPAR subunit GLR-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. GLR-1 is localized to postsynaptic clusters, and mutants for the BTB-Kelch protein KEL-8 have increased GLR-1 levels at clusters, whereas the levels and localization of other synaptic proteins seem normal. KEL-8 is a neuronal protein and is localized to sites adjacent to GLR-1 postsynaptic clusters along the ventral cord neurites. KEL-8 is required for the ubiquitin-mediated turnover of GLR-1 subunits, and kel-8 mutants show an increased frequency of spontaneous reversals in locomotion, suggesting increased levels of GLR-1 are present at synapses. KEL-8 binds to CUL-3, a Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligase subunit that we also find mediates GLR-1 turnover. Our findings indicate that KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligases that is required for the proteolysis of GLR-1 receptors and suggest a novel postmitotic role in neurons for Kelch/CUL3 ubiquitin ligases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Distinct LIN-10 domains are required for its neuronal function, its epithelial function, and its synaptic localization.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1417-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0885. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15647374 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin and AP180 regulate the abundance of GLR-1 glutamate receptors at postsynaptic elements in C. elegans.Neuron. 2002 Jul 3;35(1):107-20. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00749-3. Neuron. 2002. PMID: 12123612
-
The anaphase-promoting complex regulates the abundance of GLR-1 glutamate receptors in the ventral nerve cord of C. elegans.Curr Biol. 2004 Nov 23;14(22):2057-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.010. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15556870
-
Synaptic plasticity regulated by protein-protein interactions and posttranslational modifications.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;297:1-43. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394308-8.00001-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22608556 Review.
-
Cullin 3, a cellular scripter of the non-proteolytic ubiquitin code.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Sep;93:100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30586619 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia regulates glutamate receptor trafficking through an HIF-independent mechanism.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 21;31(6):1379-93. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.499. Epub 2012 Jan 17. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22252129 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (Ufm1) cascade of Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10661-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.458000. Epub 2013 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23449979 Free PMC article.
-
BTB-Kelch proteins and ubiquitination of kainate receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;717:115-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9557-5_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21713671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cul3 ubiquitin ligase engages Insomniac as an adaptor to impact sleep and synaptic homeostasis.PLoS Genet. 2025 Jan 22;21(1):e1011574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011574. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 39841692 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination in postsynaptic function and plasticity.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:179-210. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104129. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20604708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aarts, M. M., and Tymianski, M. (2004). Molecular mechanisms underlying specificity of excitotoxic signaling in neurons. Curr. Mol. Med. 4, 137–147. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J., Kelso, R., and Cooley, L. (2000). The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 17–24. - PubMed
-
- Bork, P., and Doolittle, R. F. (1994). Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J. Mol. Biol. 236, 1277–1282. - PubMed
-
- Bredt, D. S., and Nicoll, R. A. (2003). AMPA receptor trafficking at excitatory synapses. Neuron 40, 361–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

