KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for CUL3-dependent ubiquitin ligase that regulates synaptic glutamate receptor turnover
- PMID: 16394099
- PMCID: PMC1382314
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0794
KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for CUL3-dependent ubiquitin ligase that regulates synaptic glutamate receptor turnover
Abstract
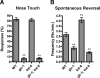
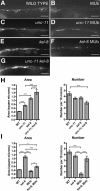
The regulated localization of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) to synapses is an important component of synaptic signaling and plasticity. Regulated ubiquitination and endocytosis determine the synaptic levels of AMPARs, but it is unclear which factors conduct these processes. To identify genes that regulate AMPAR synaptic abundance, we screened for mutants that accumulate high synaptic levels of the AMPAR subunit GLR-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. GLR-1 is localized to postsynaptic clusters, and mutants for the BTB-Kelch protein KEL-8 have increased GLR-1 levels at clusters, whereas the levels and localization of other synaptic proteins seem normal. KEL-8 is a neuronal protein and is localized to sites adjacent to GLR-1 postsynaptic clusters along the ventral cord neurites. KEL-8 is required for the ubiquitin-mediated turnover of GLR-1 subunits, and kel-8 mutants show an increased frequency of spontaneous reversals in locomotion, suggesting increased levels of GLR-1 are present at synapses. KEL-8 binds to CUL-3, a Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligase subunit that we also find mediates GLR-1 turnover. Our findings indicate that KEL-8 is a substrate receptor for Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligases that is required for the proteolysis of GLR-1 receptors and suggest a novel postmitotic role in neurons for Kelch/CUL3 ubiquitin ligases.
Figures




References
-
- Aarts, M. M., and Tymianski, M. (2004). Molecular mechanisms underlying specificity of excitotoxic signaling in neurons. Curr. Mol. Med. 4, 137–147. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J., Kelso, R., and Cooley, L. (2000). The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 17–24. - PubMed
-
- Bork, P., and Doolittle, R. F. (1994). Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J. Mol. Biol. 236, 1277–1282. - PubMed
-
- Bredt, D. S., and Nicoll, R. A. (2003). AMPA receptor trafficking at excitatory synapses. Neuron 40, 361–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

