MPP6 is an exosome-associated RNA-binding protein involved in 5.8S rRNA maturation
- PMID: 16396833
- PMCID: PMC1310903
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki982
MPP6 is an exosome-associated RNA-binding protein involved in 5.8S rRNA maturation
Abstract
The exosome is a complex of 3'-->5' exoribonucleases which is involved in many RNA metabolic processes. To regulate these functions distinct proteins are believed to recruit the exosome to specific substrate RNAs. Here, we demonstrate that M-phase phosphoprotein 6 (MPP6), a protein reported previously to co-purify with the TAP-tagged human exosome, accumulates in the nucleoli of HEp-2 cells and associates with a subset of nuclear exosomes as evidenced by co-immunoprecipitation and biochemical fractionation experiments. In agreement with its nucleolar accumulation, siRNA-mediated knock-down experiments revealed that MPP6 is involved in the generation of the 3' end of the 5.8S rRNA. The accumulation of the same processing intermediates after reducing the levels of either MPP6 or exosome components strongly suggests that MPP6 is required for the recruitment of the exosome to the pre-rRNA. Interestingly, MPP6 appeared to display RNA-binding activity in vitro with a preference for pyrimidine-rich sequences, and to bind to the ITS2 element of pre-rRNAs. Our data indicate that MPP6 is a nucleolus-specific exosome co-factor required for its role in the maturation of 5.8S rRNA.
Figures





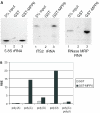

References
-
- Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Shevchenko A., Mann M., Tollervey D. The exosome: a conserved eukaryotic RNA processing complex containing multiple 3′→5′ exoribonucleases. Cell. 1997;91:457–466. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Tollervey D. The 3′ end of yeast 5.8S rRNA is generated by an exonuclease processing mechanism. Genes Dev. 1996;10:502–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

