Generation of a physiological sympathetic motor rhythm in the rat following spinal application of 5-HT
- PMID: 16396930
- PMCID: PMC1796786
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.100677
Generation of a physiological sympathetic motor rhythm in the rat following spinal application of 5-HT
Abstract
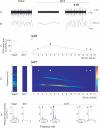
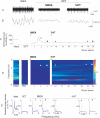
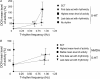
When applied in vitro to various CNS structures 5-HT and/or NMDA have been observed to generate rhythmic nervous activity. In contrast, reports of similar in vivo actions are relatively rare. Here we describe a physiological sympathetic motor rhythm regulating the thermoregulatory circulation of the rat tail (T-rhythm; 0.40-1.20 Hz) that can be elicited following intrathecal (i.t.) application of 5-HT to an in situ'isolated' spinal cord preparation (anaesthetized rats spinalized at T10-T11 and cauda equina cut). i.t. injections were delivered to L1 as sympathetic neuronal activity to the tail (SNAT) arises from preganglionic neurones at T11-L2. SNAT was abolished after spinal transection (n = 18) and it did not return spontaneously. The administration of 5-HT (250 nmol) generated rhythmic sympathetic discharges (n = 6). The mean frequency of the T-like rhythm during the highest level of activity was 0.88 +/- 0.04 Hz which was not significantly different from the T-rhythm frequency observed in intact animals (0.77 +/- 0.02 Hz; P > 0.05 n = 16). In contrast, NMDA (1 micromol) generated an irregular tonic activity, but it failed to generate a T-like rhythm (n = 9), even though the mean levels of activity were not significantly different to those produced by 5-HT. However, 5-HT (250 nmol) applied after NMDA generated a T-like rhythm (0.95 +/- 0.11 Hz, n = 6). Our observations support the idea that 5-HT released from rostral ventromedial medullary neurones, known to innervate sympathetic preganglionic neurones, can induce sympathetic rhythmic activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serotonin potentiates sympathetic responses evoked by spinal NMDA.J Physiol. 2006 Dec 1;577(Pt 2):525-37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116574. Epub 2006 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16973701 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous sympathetic motor rhythms in the decerebrate rat.Neuroscience. 2003;117(4):981-9. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00969-7. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12654350
-
The spinally mediated 10-Hz rhythm in the sympathetic nerve activity of cats.J Auton Nerv Syst. 1995 Aug 4;54(2):89-103. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(94)00194-o. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1995. PMID: 7499730
-
Sympathetic rhythms and nervous integration.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Apr;34(4):356-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04587.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17324150 Review.
-
CNS cell groups projecting to sympathetic outflow of tail artery: neural circuits involved in heat loss in the rat.Brain Res. 1998 Mar 9;786(1-2):153-64. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)01437-6. Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9554992
Cited by
-
Spontaneous rhythmogenic capabilities of sympathetic neuronal assemblies in the rat spinal cord slice.Neuroscience. 2010 Oct 27;170(3):827-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.007. Epub 2010 Jul 25. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20650307 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-tasking in the spinal cord--do 'sympathetic' interneurones work harder than we give them credit for?J Physiol. 2007 May 1;580(Pt.3):723-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.129429. Epub 2007 Mar 8. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17347266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational solution of spike overlapping using data-based subtraction algorithms to resolve synchronous sympathetic nerve discharge.Front Comput Neurosci. 2013 Oct 31;7:149. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2013.00149. eCollection 2013. Front Comput Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198782 Free PMC article.
-
What can we learn about neural control of the cardiovascular system by studying rhythms in sympathetic nerve activity?Int J Psychophysiol. 2016 May;103:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2015.02.015. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Int J Psychophysiol. 2016. PMID: 25681532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple thermoregulatory effectors with independent central controls.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 May;109(1):27-33. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1295-z. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19949811 Review.
References
-
- Alford S, Schwartz E, Viana di Prisco G. The pharmacology of vertebrate spinal central pattern generators. Neuroscientist. 2003;3:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky YI. Cellular and network properties in the functioning of the nervous system: from central pattern generators to cognition. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2003;41:229–267. - PubMed
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL. ‘Rapid’ rhythmic discharges of sympathetic nerves: sources, mechanisms of generation, and physiological relevance. J Biol Rhythms. 2000;15:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G, Draguhn A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science. 2004;304:1926–1929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

