Structure of the parainfluenza virus 5 F protein in its metastable, prefusion conformation
- PMID: 16397490
- PMCID: PMC7095149
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04322
Structure of the parainfluenza virus 5 F protein in its metastable, prefusion conformation
Abstract
Enveloped viruses have evolved complex glycoprotein machinery that drives the fusion of viral and cellular membranes, permitting entry of the viral genome into the cell. For the paramyxoviruses, the fusion (F) protein catalyses this membrane merger and entry step, and it has been postulated that the F protein undergoes complex refolding during this process. Here we report the crystal structure of the parainfluenza virus 5 F protein in its prefusion conformation, stabilized by the addition of a carboxy-terminal trimerization domain. The structure of the F protein shows that there are profound conformational differences between the pre- and postfusion states, involving transformations in secondary and tertiary structure. The positions and structural transitions of key parts of the fusion machinery, including the hydrophobic fusion peptide and two helical heptad repeat regions, clarify the mechanism of membrane fusion mediated by the F protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Coordinates and structure factor amplitudes have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID code 2B9B). Reprints and permissions information is available at
Figures
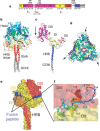
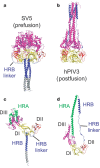
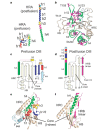
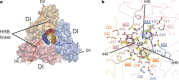
References
-
- Lamb RA, Kolakofsky D. Fields Virology. 2001. pp. 1305–1340.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

