A peptide-loaded dendritic cell based cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) vaccination strategy using peptides that span SIV Tat, Rev, and Env overlapping reading frames
- PMID: 16398928
- PMCID: PMC1360091
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-1
A peptide-loaded dendritic cell based cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) vaccination strategy using peptides that span SIV Tat, Rev, and Env overlapping reading frames
Abstract
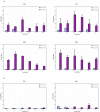
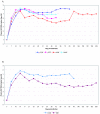
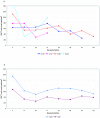
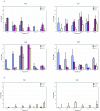
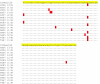
CTL based vaccine strategies in the macaque model of AIDS have shown promise in slowing the progression to disease. However, rapid CTL escape viruses can emerge rendering such vaccination useless. We hypothesized that such escape is made more difficult if the immunizing CTL epitope falls within a region of the virus that has a high density of overlapping reading frames which encode several viral proteins. To test this hypothesis, we immunized macaques using a peptide-loaded dendritic cell approach employing epitopes in the second coding exon of SIV Tat which spans reading frames for both Env and Rev. We report here that autologous dendritic cells, loaded with SIV peptides from Tat, Rev, and Env, induced a distinct cellular immune response measurable ex vivo. However, conclusive in vivo control of a challenge inoculation of SIVmac239 was not observed suggesting that CTL epitopes within densely overlapping reading frames are also subject to escape mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Smith SM, Singh M, Jeang KT. A vaccine for HIV / AIDS : challenges and progress. In: Meyers RA, editor. Encyclopedia of Molecular Cell Biology and Molecular Medicine. New York, WILEY-VCH Verlag; 2005.
-
- Barouch DH, Kunstman J, Glowczwskie J, Kunstman KJ, Egan MA, Peyerl FW, Santra S, Kuroda MJ, Schmitz JE, Beaudry K, Krivulka GR, Lifton MA, Gorgone DA, Wolinsky SM, Letvin NL. Viral escape from dominant simian immunodeficiency virus epitope-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in DNA-vaccinated rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 2003;77:7367–7375. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.13.7367-7375.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen TM, Jing P, Calore B, Horton H, O'Connor DH, Hanke T, Piekarczyk M, Ruddersdorf R, Mothe BR, Emerson C, Wilson N, Lifson JD, Belyakov IM, Berzofsky JA, Wang C, Allison DB, Montefiori DC, Desrosiers RC, Wolinsky S, Kunstman KJ, Altman JD, Sette A, McMichael AJ, Watkins DI. Effects of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) directed against a single simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) Gag CTL epitope on the course of SIVmac239 infection. J Virol. 2002;76:10507–10511. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.20.10507-10511.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mothe BR, Horton H, Carter DK, Allen TM, Liebl ME, Skinner P, Vogel TU, Fuenger S, Vielhuber K, Rehrauer W, Wilson N, Franchini G, Altman JD, Haase A, Picker LJ, Allison DB, Watkins DI. Dominance of CD8 responses specific for epitopes bound by a single major histocompatibility complex class I molecule during the acute phase of viral infection. J Virol. 2002;76:875–884. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.2.875-884.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

