The caCORE Software Development Kit: streamlining construction of interoperable biomedical information services
- PMID: 16398930
- PMCID: PMC1379637
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-6-2
The caCORE Software Development Kit: streamlining construction of interoperable biomedical information services
Abstract
Background: Robust, programmatically accessible biomedical information services that syntactically and semantically interoperate with other resources are challenging to construct. Such systems require the adoption of common information models, data representations and terminology standards as well as documented application programming interfaces (APIs). The National Cancer Institute (NCI) developed the cancer common ontologic representation environment (caCORE) to provide the infrastructure necessary to achieve interoperability across the systems it develops or sponsors. The caCORE Software Development Kit (SDK) was designed to provide developers both within and outside the NCI with the tools needed to construct such interoperable software systems.
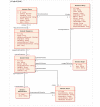
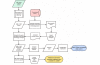
Results: The caCORE SDK requires a Unified Modeling Language (UML) tool to begin the development workflow with the construction of a domain information model in the form of a UML Class Diagram. Models are annotated with concepts and definitions from a description logic terminology source using the Semantic Connector component. The annotated model is registered in the Cancer Data Standards Repository (caDSR) using the UML Loader component. System software is automatically generated using the Codegen component, which produces middleware that runs on an application server. The caCORE SDK was initially tested and validated using a seven-class UML model, and has been used to generate the caCORE production system, which includes models with dozens of classes. The deployed system supports access through object-oriented APIs with consistent syntax for retrieval of any type of data object across all classes in the original UML model. The caCORE SDK is currently being used by several development teams, including by participants in the cancer biomedical informatics grid (caBIG) program, to create compatible data services. caBIG compatibility standards are based upon caCORE resources, and thus the caCORE SDK has emerged as a key enabling technology for caBIG.
Conclusion: The caCORE SDK substantially lowers the barrier to implementing systems that are syntactically and semantically interoperable by providing workflow and automation tools that standardize and expedite modeling, development, and deployment. It has gained acceptance among developers in the caBIG program, and is expected to provide a common mechanism for creating data service nodes on the data grid that is under development.
Figures

References
-
- ISO/IEC 11179, Information Technology -- Metadata Registries (MDR) 1999. http://metadata-standards.org/11179/
-
- caCORE 3.0. 2005. http://ncicb.nci.nih.gov/core
-
- The NCI Cancer Models Database. 2005. http://cancermodels.nci.nih.gov
-
- caWorkbench - A Platform for Integrated Genomics. 2005. http://amdec-bioinfo.cu-genome.org/html/caWorkBench3.htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

