Interleukin-27R (WSX-1/T-cell cytokine receptor) gene-deficient mice display enhanced resistance to leishmania donovani infection but develop severe liver immunopathology
- PMID: 16400019
- PMCID: PMC1592683
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050013
Interleukin-27R (WSX-1/T-cell cytokine receptor) gene-deficient mice display enhanced resistance to leishmania donovani infection but develop severe liver immunopathology
Abstract
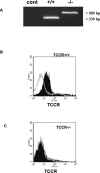
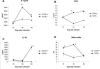
The interleukin-27 (IL-27)/T-cell cytokine receptor (TCCR) pathway plays an important role in development of protective immunity against cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania major. In this study, we analyzed the role of IL-27/TCCR pathway in the host defense against visceral leishmaniasis (VL) by monitoring the course of L. donovani infection in TCCR-deficient C57BL/6 (TCCR-/-) mice. TCCR-/- mice mounted a robust inflammatory response, produced high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and developed severe liver pathology after L. donovani infection that eventually resolved. Interestingly, L. donovani-infected TCCR-/- mice controlled the parasite growth in their organs significantly faster than similarly infected TCCR+/+ mice. Adoptive cell transfer and cell depletion studies revealed that CD4(+) T cells were involved in mediating liver immunopathology and controlling L. donovani growth in TCCR-/- mice. These results indicate that the IL-27/TCCR pathway is not essential for the induction of protective Th1 response during VL but is involved in mediating susceptibility to L. donovani. Additionally, the data demonstrate that although the IL-27/TCCR interaction limits the severity of liver inflammation during VL by controlling CD4(+) T-cell activity, it is not required for the resolution of hepatic immunopathology.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Essential role for IL-27 receptor signaling in prevention of Th1-mediated immunopathology during malaria infection.J Immunol. 2010 Aug 15;185(4):2482-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904019. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20631310
-
IL-12 gene-deficient C57BL/6 mice are susceptible to Leishmania donovani but have diminished hepatic immunopathology.Eur J Immunol. 2000 Mar;30(3):834-9. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200003)30:3<834::AID-IMMU834>3.0.CO;2-9. Eur J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10741399
-
Lack of CXCR3 delays the development of hepatic inflammation but does not impair resistance to Leishmania donovani.J Infect Dis. 2007 Jun 1;195(11):1713-7. doi: 10.1086/516787. Epub 2007 Apr 16. J Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17471442
-
Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in human Leishmania donovani infections.Immunol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;71 ( Pt 6):583-7. doi: 10.1038/icb.1993.64. Immunol Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8314285 Review.
-
The role of CD4+ T cells in visceral leishmaniasis; new and emerging roles for NKG7 and TGFβ.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 31;14:1414493. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1414493. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38881737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential.Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Dec;14(12):1131-1141. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 26253381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E2 inhibits Tr1 cell differentiation through suppression of c-Maf.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 12;12(6):e0179184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179184. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28604806 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of Th17 responses.Semin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):394-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.11.006. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18221887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-27 Induced by Select Candida spp. via TLR7/NOD2 Signaling and IFN-β Production Inhibits Fungal Clearance.J Immunol. 2016 Jul 1;197(1):208-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501204. Epub 2016 Jun 3. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27259855 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma Interferon-Regulated Chemokines in Leishmania donovani Infection in the Liver.Infect Immun. 2016 Dec 29;85(1):e00824-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00824-16. Print 2017 Jan. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27795366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander J, Satoskar AR, Russell DG. Leishmania species: models of intracellular parasitism. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:2993–3002. - PubMed
-
- Villarino AV, Huang E, Hunter CA. Understanding the pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of IL-27. J Immunol. 2004;173:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, Gilbert J, Hibbert L, Churakova T, Travis M, Vaisberg E, Blumenschein WM, Mattson JD, Wagner JL, To W, Zurawski S, McClanahan TK, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, de Waal MR, Rennick D, Kastelein RA. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity. 2002;16:779–790. - PubMed
-
- Sprecher CA, Grant FJ, Baumgartner JW, Presnell SR, Schrader SK, Yamagiwa T, Whitmore TE, O’Hara PJ, Foster DF. Cloning and characterization of a novel class I cytokine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;246:82–90. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Hibbert L, Mattson J, Rosales R, Vaisberg E, Bazan JF, Phillips JH, McClanahan TK, de Waal MR, Kastelein RA. WSX-1 and glycoprotein 130 constitute a signal-transducing receptor for IL-27. J Immunol. 2004;172:2225–2231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

