Serum resistance-associated protein blocks lysosomal targeting of trypanosome lytic factor in Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 16400175
- PMCID: PMC1360256
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.5.1.132-139.2006
Serum resistance-associated protein blocks lysosomal targeting of trypanosome lytic factor in Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
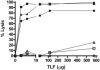
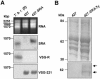
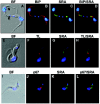
Trypanosoma brucei brucei is the causative agent of nagana in cattle and can infect a wide range of mammals but is unable to infect humans because it is susceptible to the innate cytotoxic activity of normal human serum. A minor subfraction of human high-density lipoprotein (HDL) containing apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I), apolipoprotein L-I (apoL-I), and haptoglobin-related protein (Hpr) provides this innate protection against T. b. brucei infection. This HDL subfraction, called trypanosome lytic factor (TLF), kills T. b. brucei following receptor binding, endocytosis, and lysosomal localization. Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense, which is morphologically and physiologically indistinguishable from T. b. brucei, is resistant to TLF-mediated killing and causes human African sleeping sickness. Human infectivity by T. b. rhodesiense correlates with the evolution of a resistance-associated protein (SRA) that is able to ablate TLF killing. To examine the mechanism of TLF resistance, we transfected T. b. brucei with an epitope-tagged SRA gene. Transfected T. b. brucei expressed SRA mRNA at levels comparable to those in T. b. rhodesiense and was highly resistant to TLF. In the SRA-transfected cells, intracellular trafficking of TLF was altered, with TLF being mainly localized to a subset of SRA-containing cytoplasmic vesicles but not to the lysosome. These results indicate that the cellular distribution of TLF is influenced by SRA expression and may directly determine the organism's susceptibility to TLF.
Figures




References
-
- Bangs, J. D., L. Uyetake, M. J. Brickman, A. E. Balber, and J. C. Boothroyd. 1993. Molecular cloning and cellular localization of a BiP homologue in Trypanosoma brucei. Divergent ER retention signals in a lower eukaryote. J. Cell Sci. 105:1101-1113. - PubMed
-
- Bastin, P., Z. Bagherzadeh, K. R. Matthews, and K. Gull. 1996. A novel epitope tag system to study protein targeting and organelle biogenesis in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 77:235-239. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, J. R., M. Shimamura, and S. L. Hajduk. 2001. Insight into the mechanism of trypanosome lytic factor-1 killing of Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 118:33-40. - PubMed
-
- Black, S. J., J. R. Seed, and N. B. Murphy. 2001. Innate and acquired resistance to African trypanosomiasis. J. Parasitol. 87:1-9. - PubMed
-
- Burnette, W. N. 1981. “Western blotting”: electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal. Biochem. 112:195-203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

