The akuB(KU80) mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 16400184
- PMCID: PMC1360264
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.5.1.207-211.2006
The akuB(KU80) mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
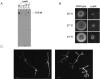
To increase the frequency of homologous recombination, we inactivated the KU80 homologue in Aspergillus fumigatus (named akuB(KU80)). Homologous integration reached about 80% for both calcineurin A (calA) and polyketide synthase pksP (alb1) genes in the akuB(KU80) mutant to 3 and 5%, respectively, when using a wild-type A. fumigatus strain. Deletion of akuB(KU80) had no influence on pathogenicity in a low-dose murine infection model.
Figures
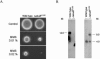

References
-
- D'Enfert, C. 1996. Selection of multiple disruption events in Aspergillus fumigatus using the orotidine-5′-decarboxylase gene, pyrG, as a unique transformation marker. Curr. Genet. 30:76-82. - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W. 1996. Diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis. Curr. Clin. Top. Infect. Dis. 16:277-299. - PubMed
-
- Kafer, E. 1977. Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergilllus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv. Genet. 19:33-131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

