Genomewide linkage scan of 409 European-ancestry and African American families with schizophrenia: suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-p21.2 and 11p13.1-q14.1 in the combined sample
- PMID: 16400611
- PMCID: PMC1380238
- DOI: 10.1086/500272
Genomewide linkage scan of 409 European-ancestry and African American families with schizophrenia: suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-p21.2 and 11p13.1-q14.1 in the combined sample
Abstract
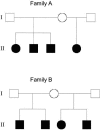
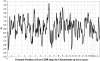
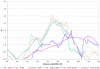
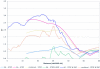
We report the clinical characteristics of a schizophrenia sample of 409 pedigrees--263 of European ancestry (EA) and 146 of African American ancestry (AA)--together with the results of a genome scan (with a simple tandem repeat polymorphism interval of 9 cM) and follow-up fine mapping. A family was required to have a proband with schizophrenia (SZ) and one or more siblings of the proband with SZ or schizoaffective disorder. Linkage analyses included 403 independent full-sibling affected sibling pairs (ASPs) (279 EA and 124 AA) and 100 all-possible half-sibling ASPs (15 EA and 85 AA). Nonparametric multipoint linkage analysis of all families detected two regions with suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-q12 and 11p11.2-q22.3 (empirical Z likelihood-ratio score [Z(lr)] threshold >/=2.65) and, in exploratory analyses, two other regions at 4p16.1-p15.32 in AA families and at 5p14.3-q11.2 in EA families. The most significant linkage peak was in chromosome 8p; its signal was mainly driven by the EA families. Z(lr) scores >2.0 in 8p were observed from 30.7 cM to 61.7 cM (Center for Inherited Disease Research map locations). The maximum evidence in the full sample was a multipoint Z(lr) of 3.25 (equivalent Kong-Cox LOD of 2.30) near D8S1771 (at 52 cM); there appeared to be two peaks, both telomeric to neuregulin 1 (NRG1). There is a paracentric inversion common in EA individuals within this region, the effect of which on the linkage evidence remains unknown in this and in other previously analyzed samples. Fine mapping of 8p did not significantly alter the significance or length of the peak. We also performed fine mapping of 4p16.3-p15.2, 5p15.2-q13.3, 10p15.3-p14, 10q25.3-q26.3, and 11p13-q23.3. The highest increase in Z(lr) scores was observed for 5p14.1-q12.1, where the maximum Z(lr) increased from 2.77 initially to 3.80 after fine mapping in the EA families.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A reanalysis of 409 European-Ancestry and African American schizophrenia pedigrees reveals significant linkage to 8p23.3 with evidence of locus heterogeneity.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008 Oct 5;147B(7):1080-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30722. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008. PMID: 18361422
-
Genome scan of schizophrenia families in a large Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study sample: evidence for linkage to 18p11.32 and for racial heterogeneity on chromosomes 6 and 14.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005 Nov 5;139B(1):91-100. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30213. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005. PMID: 16152571
-
Genetics of recurrent early-onset major depression (GenRED): significant linkage on chromosome 15q25-q26 after fine mapping with single nucleotide polymorphism markers.Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Feb;164(2):259-64. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2007.164.2.259. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17267788
-
Association between the neuregulin 1 gene and schizophrenia: a systematic review.Schizophr Bull. 2005 Jul;31(3):613-7. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbi043. Epub 2005 Aug 4. Schizophr Bull. 2005. PMID: 16081509
-
Genome scans and microarrays: converging on genes for schizophrenia?Genome Biol. 2002;3(4):REVIEWS1011. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-4-reviews1011. Epub 2002 Mar 27. Genome Biol. 2002. PMID: 11983064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome association studies of neuropsychiatric traits in African Americans implicate PRMT7 in schizophrenia.PeerJ. 2019 Sep 26;7:e7778. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7778. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31579629 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated endogenous GDNF induces altered dopamine signalling in mice and correlates with clinical severity in schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;27(8):3247-3261. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01554-2. Epub 2022 May 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35618883 Free PMC article.
-
NOS1AP in schizophrenia.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2008 Apr;10(2):158-63. doi: 10.1007/s11920-008-0027-0. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2008. PMID: 18474209 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis reveals schizophrenia-associated dysregulation of immune pathways in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.J Psychiatr Res. 2013 Apr;47(4):425-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 4. J Psychiatr Res. 2013. PMID: 23218666 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting schizophrenia linkage data in the NIMH Repository: reanalysis of regularized data across multiple studies.Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Mar;171(3):350-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.11121766. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24170318 Free PMC article.
References
Web Resources
-
- Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR), http://www.cidr.jhmi.edu/
-
- Consensus Coding DNA Sequence (CCDS) database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/CCDS/ (for March 2005 report)
-
- dbSNP, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/ (for build 34)
-
- HapMap, http://www.hapmap.org/
-
- NIMH Center for Collaborative Genetics Studies of Mental Disorders, http://zork.wustl.edu/nimh/
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. APA, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH60879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH61675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH60870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

