Facilitating RNA structure prediction with microarrays
- PMID: 16401087
- PMCID: PMC4070881
- DOI: 10.1021/bi051409+
Facilitating RNA structure prediction with microarrays
Abstract
Determining RNA secondary structure is important for understanding structure-function relationships and identifying potential drug targets. This paper reports the use of microarrays with heptamer 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides to probe the secondary structure of an RNA and thereby improve the prediction of that secondary structure. When experimental constraints from hybridization results are added to a free-energy minimization algorithm, the prediction of the secondary structure of Escherichia coli 5S rRNA improves from 27 to 92% of the known canonical base pairs. Optimization of buffer conditions for hybridization and application of 2'-O-methyl-2-thiouridine to enhance binding and improve discrimination between AU and GU pairs are also described. The results suggest that probing RNA with oligonucleotide microarrays can facilitate determination of secondary structure.
Figures
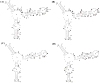

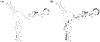
 - middle site of strong binding;
- middle site of strong binding;
 - middle site of medium binding.
- middle site of medium binding.

 - middle site of strong binding;
- middle site of strong binding;
 - middle site of medium binding.
- middle site of medium binding.References
-
- Fox GE, Woese CR. 5S-RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975;256:505–507. - PubMed
-
- Pace NR, Thomas BC, Woese CR. Probing RNA structure, function, and history by comparative analysis. In: Gesteland RF, Cech TR, Atkins JF, editors. The RNA World. Cold Spring Harbor Press; New York: 1999. pp. 113–141.
-
- Goertzen LR, Cannone JJ, Gutell RR, Jansen RK. ITS secondary structure derived from comparative analysis: implications for sequence alignment and phylogeny of the Asteraceae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2003;29:216–234. - PubMed
-
- Cannone JJ, Subramanian S, Schnare MN, Collett JR, D’Souza LM, Du YS, Feng B, Lin N, Madabusi LV, Muller KM, Pande N, Shang ZD, Yu N, Gutell RR. The Comparative RNA Web (CRW) Site: an online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs. Bmc Bioinformatics. 2002:3. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

