TC-2559 excites dopaminergic neurones in the ventral tegmental area by stimulating alpha4beta2-like nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in anaesthetised rats
- PMID: 16402043
- PMCID: PMC1616994
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706621
TC-2559 excites dopaminergic neurones in the ventral tegmental area by stimulating alpha4beta2-like nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in anaesthetised rats
Abstract
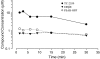
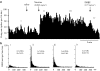
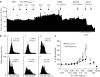
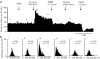
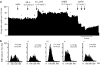
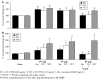
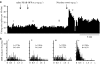
1. The in vivo effects of a selective partial agonist for neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) alpha4beta2 subtype, TC-2559, characterised recently in in vitro preparations, have been profiled. The brain bioavailability of TC-2559 and its effects on the spontaneous firing and bursting properties of the dopaminergic (DAergic) neurones recorded extracellularly in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) were studied following systemic administration in anaesthetised rats. 2. Cumulative doses of TC-2559 (0.021-1.36 mg kg(-1), i.v.) increased both the firing and bursting activities of VTA DA neurones. The effect of bolus doses of TC-2559 of 0.66 or 1.32 mg kg(-1), i.v., was approximately equivalent to that of 0.0665 mg kg(-1), i.v. nicotine. 3. The excitation evoked by both nicotine and TC-2559 was fully reversed by DHbetaE (0.39-0.77 mg kg(-1), i.v.), an alpha4beta2-subtype-preferring nicotinic antagonist, and application of nicotine after DHbetaE failed to evoke any excitation. MLA (0.23 mg kg(-1), i.v.), an alpha7 selective antagonist, failed to alter TC-2559-evoked excitation and bursting activities, and a novel alpha7 agonist (PSAB-OFP; 0.23 mg kg(-1), i.v.) was also without effect. 4. The present results indicated that TC-2559 fully mimics nicotine by increasing both the excitability and bursting behaviour of VTA DA neurones, effects that are predominantly due to activation of alpha4beta2-like nAChRs. 5. TC-2559 has been demonstrated to be a useful in vivo pharmacological tool for studying the alpha4beta2 subtype of nicotinic receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The nicotinic alpha 4 beta 2 receptor selective agonist, TC-2559, increases dopamine neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area of rat midbrain slices.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Sep;45(3):334-44. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00189-8. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12871651
-
Distinctive nicotinic acetylcholine receptor functional phenotypes of rat ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons.J Physiol. 2009 Jan 15;587(2):345-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.162743. Epub 2008 Dec 1. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19047205 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine potentiation of excitatory inputs to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 May 4;31(18):6710-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5671-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21543600 Free PMC article.
-
Tribute to: Self-administered nicotine activates the mesolimbic dopamine system through the ventral tegmental area [William Corrigall, Kathleen Coen and Laurel Adamson, Brain Res. 653 (1994) 278-284].Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:61-4. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.064. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26867702 Review.
-
Cortical control of VTA function and influence on nicotine reward.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;86(8):1173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933294 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of age on nicotinic cholinergic regulation of blood flow in rat's olfactory bulb and neocortex.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;74(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00913-8. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38491428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial agonists for α4β2 nicotinic receptors stimulate dopaminergic neuron firing with relatively enhanced maximal effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4):1006-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01628.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21838750 Free PMC article.
-
α6β2* and α4β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as drug targets for Parkinson's disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Dec;63(4):938-66. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003269. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21969327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced inhibitory synaptic transmission in the spinal dorsal horn mediates antinociceptive effects of TC-2559.Mol Pain. 2011 Aug 4;7:56. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-56. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21816108 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular effects of activation of central alpha7 and alpha4beta2 nAChRs: a role for vasopressin in anaesthetized rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr;153(8):1728-38. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.47. Epub 2008 Feb 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18297099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ASTLES P.C., BAKER S.R., BOOT J.R., BROAD L.M., DELL C.P., KEENAN M. Recent progress in the development of subtype selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands. Curr. Drug Targets CNS & Neurol. Disord. 2002;1:337–348. - PubMed
-
- AZAM L., WINZER-SERHAN U.H., CHEN Y., LESLIE F.M. Expression of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit mRNAs within midbrain dopamine neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002;444:260–274. - PubMed
-
- BALFOUR D.J.K., BIRRELL C.E., MORAN R.J., BENWELL E.M. Effects of D-CPPene on mesoaccumbens dopamine responses to nicotine in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996;316:153–156. - PubMed
-
- BALFOUR D.J.K., WRIGHT A.E., BENWELL E.M., BIRRELL C.E. The putative role of extra-synaptic mesolimbic dopamine in the neurobiology of nicotine dependence. Behav. Brain Res. 2000;113:73–83. - PubMed
-
- BENCHERIF M., BANE A.J., MILLER C.H., DULL G.M., GATTO G.J. TC-2559: A novel orally active ligand selective at neuronal acetylcholine receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;409:45–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

