Cytochrome P450 and xenobiotic receptor humanized mice
- PMID: 16402898
- PMCID: PMC1440291
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.100007
Cytochrome P450 and xenobiotic receptor humanized mice
Abstract
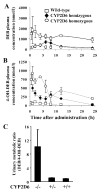
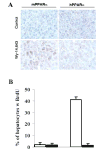
Most xenobiotics that enter the body are subjected to metabolism that functions primarily to facilitate their elimination. Metabolism of certain xenobiotics can also result in the production of electrophilic derivatives that can cause cell toxicity and transformation. Many xenobiotics can also activate receptors that in turn induce the expression of genes encoding xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes and xenobiotic transporters. However, there are marked species differences in the way mammals respond to xenobiotics, which are due in large part to molecular differences in receptors and xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes. This presents a problem in extrapolating data obtained with rodent model systems to humans. There are also polymorphisms in xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes that can impact drug therapy and cancer susceptibility. In an effort to generate more reliable in vivo systems to study and predict human response to xenobiotics, humanized mice are under development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of gene knockout and transgenic mice in the study of xenobiotic metabolism.Drug Metab Rev. 2003 Nov;35(4):319-35. doi: 10.1081/dmr-120026496. Drug Metab Rev. 2003. PMID: 14705864 Review.
-
Comparison of xenobiotic-metabolising human, porcine, rodent, and piscine cytochrome P450.Toxicology. 2017 Jan 15;375:10-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 27884721 Review.
-
Some aspects of interindividual variations in the metabolism of xenobiotics.Inflamm Res. 2003 Aug;52(8):322-33. doi: 10.1007/s00011-003-1186-4. Inflamm Res. 2003. PMID: 14504670 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 humanised mice.Hum Genomics. 2004 May;1(4):300-6. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-1-4-300. Hum Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15588489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xenobiotic response in humanized double transgenic mice expressing tetracycline-controlled transactivator and human CYP1B1.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 Nov 1;395(1):32-40. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2542. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11673863
Cited by
-
A human hepatocyte-bearing mouse: an animal model to predict drug metabolism and effectiveness in humans.PPAR Res. 2009;2009:476217. doi: 10.1155/2009/476217. Epub 2009 Oct 26. PPAR Res. 2009. PMID: 19884982 Free PMC article.
-
DIFFERENTIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY OF HUMAN SP-B GENETIC VARIANTS ON LUNG INJURY CAUSED BY BACTERIAL PNEUMONIA AND THE EFFECT OF A CHEMICALLY MODIFIED CURCUMIN.Shock. 2016 Apr;45(4):375-84. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000535. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26863117 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling as an initial approach for mechanistic studies of toxicity and tumorigenicity of herbal plants and herbal dietary supplements.J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2010 Jan;28(1):60-87. doi: 10.1080/10590500903585416. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20390968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver.Compr Physiol. 2013 Apr;3(2):977-1010. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120020. Compr Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23720337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically modified mouse models in cancer studies.Clin Transl Oncol. 2008 Dec;10(12):794-803. doi: 10.1007/s12094-008-0292-8. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19068450 Review.
References
-
- Gonzalez FJ, Gelboin HV. Role of human cytochromes P450 in the metabolic activation of chemical carcinogens and toxins. Drug Metab Rev. 1994;26:165–83. - PubMed
-
- Guengerich FP. Cytochromes P450, drugs, and diseases. Mol Interv. 2003;3:194–204. - PubMed
-
- Nebert DW, Russell DW. Clinical importance of the cytochromes P450. Lancet. 2002;360:1155–62. - PubMed
-
- Willson TM, Kliewer SA. PXR, CAR and drug metabolism. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:259–66. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez FJ, Liu SY, Yano M. Regulation of cytochrome P450 genes: molecular mechanisms. Pharmacogenetics. 1993;3:51–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

