Polymorphisms of genes coding for insulin-like growth factor 1 and its major binding proteins, circulating levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk: results from the EPIC study
- PMID: 16404426
- PMCID: PMC2361124
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602936
Polymorphisms of genes coding for insulin-like growth factor 1 and its major binding proteins, circulating levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk: results from the EPIC study
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) stimulates cell proliferation and can enhance the development of tumours in different organs. Epidemiological studies have shown that an elevated level of circulating IGF-I is associated with increased risk of breast cancer, as well as of other cancers. Most of circulating IGF-I is bound to an acid-labile subunit and to one of six insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs), among which the most important are IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-1. Polymorphisms of the IGF1 gene and of genes encoding for the major IGF-I carriers may predict circulating levels of IGF-I and have an impact on cancer risk. We tested this hypothesis with a case-control study of 807 breast cancer patients and 1588 matched control subjects, nested within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. We genotyped 23 common single nucleotide polymorphisms in IGF1, IGFBP1, IGFBP3 and IGFALS, and measured serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in samples of cases and controls. We found a weak but significant association of polymorphisms at the 5' end of the IGF1 gene with breast cancer risk, particularly among women younger than 55 years, and a strong association of polymorphisms located in the 5' end of IGFBP3 with circulating levels of IGFBP-3, which confirms previous findings. Common genetic variation in these candidate genes does not play a major role in altering breast cancer risk in Caucasians.
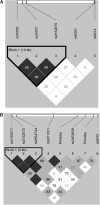
Figures
References
-
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21: 263–265 - PubMed
-
- Bingham S, Riboli E (2004) Diet and cancer – the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 206–215 - PubMed
-
- Bohlke K, Cramer DW, Trichopoulos D, Mantzoros CS (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-I in relation to premenopausal ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Epidemiology 9: 570–573 - PubMed
-
- Bruning PF, Van Doorn J, Bonfrer JM, Van Noord PA, Korse CM, Linders TC, Hart AA (1995) Insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein 3 is decreased in early-stage operable pre-menopausal breast cancer. Int J Cancer 62: 266–270 - PubMed
-
- Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH, Pollak M (1998) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279: 563–566 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

