Transrectal prostate biopsy and fiducial marker placement in a standard 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging scanner
- PMID: 16406885
- PMCID: PMC3299542
- DOI: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00065-0
Transrectal prostate biopsy and fiducial marker placement in a standard 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging scanner
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the accuracy and feasibility of a system that provides transrectal needle access to the prostate concurrent with 1.5 Tesla MRI which previously has not been possible.
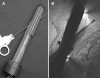
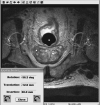
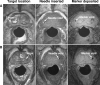
Materials and methods: In 5 patients with previously diagnosed prostate cancer, MRI guided intraprostatic placement of gold fiducial markers (4 procedures) and/or prostate biopsy (3 procedures) was performed using local anesthesia.
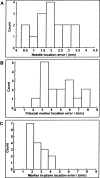
Results: Mean procedure duration was 76 minutes and all patients tolerated the intervention well. Procedure related adverse events included self-limited hematuria and hematochezia following 3 of 8 procedures (all resolved in less than 1 week). Mean needle placement accuracy was 1.9 mm for the fiducial marker placement studies and 1.8 mm for the biopsy procedures. Mean fiducial marker placement accuracy was 4.8 mm and the mean fiducial marker placement accuracy transverse to the needle direction was 2.6 mm. All patients who underwent the procedure were able to complete their course of radiotherapy without delay or complication.
Conclusions: While studies of clinical usefulness are warranted, transrectal 1.5 T MRI guided prostate biopsy and fiducial marker placement is feasible using this system, providing new opportunities for image guided diagnostic and therapeutic prostate interventions.
Figures




Comment in
-
The continuing search for meaningful prognostic information from prostate biopsy.J Urol. 2006 Jan;175(1):16-7. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00256-9. J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16406862 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yu KK, Hricak H. Imaging prostate cancer. Radiol Clin North Am. 2000;38:59. - PubMed
-
- Wefer AE, Hricak H, Vigneron DB, Coakley FV, Lu Y, Wefer J, et al. Sextant localization of prostate cancer: comparison of sextant biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging with step section histology. J Urol. 2000;164:400. - PubMed
-
- Cormack RA, Kooy H, Tempany CM, D'Amico AV. A clinical method for real-time dosimetric guidance of transperineal 125I prostate implants using interventional magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;46:207. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico AV, Tempany CM, Cormack R, Hata N, Jinzaki M, Tuncali K, et al. Transperineal magnetic resonance image guided prostate biopsy. J Urol. 2000;164:385. - PubMed
-
- Cormack RA, D'Amico AV, Hata N, Silverman S, Weinstein M, Tempany CM. Feasibility of transperineal prostate biopsy under interventional magnetic resonance guidance. Urology. 2000;56:663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

