AtGAT1, a high affinity transporter for gamma-aminobutyric acid in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 16407306
- PMCID: PMC3009663
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M510766200
AtGAT1, a high affinity transporter for gamma-aminobutyric acid in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
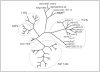
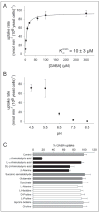
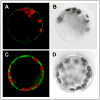
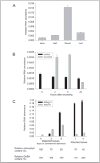
Functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana GAT1 in heterologous expression systems, i.e. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Xenopus laevis oocytes, revealed that AtGAT1 (At1g08230) codes for an H(+)-driven, high affinity gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter. In addition to GABA, other omega-aminofatty acids and butylamine are recognized. In contrast to the most closely related proteins of the proline transporter family, proline and glycine betaine are not transported by AtGAT1. AtGAT1 does not share sequence similarity with any of the non-plant GABA transporters described so far, and analyses of substrate selectivity and kinetic properties showed that AtGAT1-mediated transport is similar but distinct from that of mammalian, bacterial, and S. cerevisiae GABA transporters. Consistent with a role in GABA uptake into cells, transient expression of AtGAT1/green fluorescent protein fusion proteins in tobacco protoplasts revealed localization at the plasma membrane. In planta, AtGAT1 expression was highest in flowers and under conditions of elevated GABA concentrations such as wounding or senescence.
Figures




References
-
- Steward FC, Thompson JF, Dent CE. Science. 1949;110:439–440.
-
- Borden LA. Neurochem Int. 1996;29:335–356. - PubMed
-
- Chen N-H, Reith MA, Quick M. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2004;447:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Owens DF, Kriegstein AR. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:715–727. - PubMed
-
- Jack DL, Paulsen IT, Saier MH. Microbiology. 2000;146:1797–1814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

