Group V secretory phospholipase A2 translocates to the phagosome after zymosan stimulation of mouse peritoneal macrophages and regulates phagocytosis
- PMID: 16407308
- PMCID: PMC1820836
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M508314200
Group V secretory phospholipase A2 translocates to the phagosome after zymosan stimulation of mouse peritoneal macrophages and regulates phagocytosis
Abstract
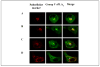
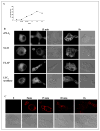
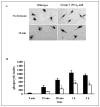
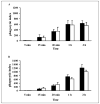
We have previously reported that group V secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) amplifies the action of cytosolic phospholipase A2(cPLA2) alpha in regulating eicosanoid biosynthesis by mouse peritoneal macrophages stimulated with zymosan (Satake, Y., Diaz, B. L., Balestrieri, B., Lam, B. K., Kanaoka, Y., Grusby, M. J., and Arm, J. P. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 16488-16494). To further understand the role of group V sPLA2, we studied its localization in resting mouse peritoneal macrophages before and after stimulation with zymosan and the effect of deletion of the gene encoding group V sPLA2 on phagocytosis of zymosan. We report that group V sPLA2 is present in the Golgi apparatus and recycling endosome in the juxtanuclear region of resting peritoneal macrophages. Upon ingestion of zymosan by mouse peritoneal macrophages, group V sPLA2 is recruited to the phagosome. There it co-localizes with cPLA2alpha, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein, and leukotriene C4 synthase. Using immunostaining for the cysteinyl leukotrienes in carbodiimide-fixed cells, we show, for the first time, that the phagosome is a site of cysteinyl leukotriene formation. Furthermore, peritoneal macrophages from group V sPLA2-null mice demonstrated a >50% attenuation in phagocytosis of zymosan particles, which was restored by adenoviral expression of group V sPLA2 but IIA not group sPLA2. These data demonstrate that group V sPLA2 contributes to the innate immune response both through regulation of eicosanoid generation in response to a phagocytic stimulus and also as a component of the phagocytic machinery.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of group V phospholipase A2 in zymosan-induced eicosanoid generation and vascular permeability revealed by targeted gene disruption.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 16;279(16):16488-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313748200. Epub 2004 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14761945 Free PMC article.
-
Group V secretory phospholipase A2 modulates phagosome maturation and regulates the innate immune response against Candida albicans.J Immunol. 2009 Apr 15;182(8):4891-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803776. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19342668 Free PMC article.
-
Group V secretory PLA2 regulates TLR2-dependent eicosanoid generation in mouse mast cells through amplification of ERK and cPLA2alpha activation.Blood. 2007 Jul 15;110(2):561-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-052258. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17369491 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of eicosanoid biosynthesis in the macrophage. Involvement of protein tyrosine phosphorylation and modulation by selective protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 9;45(3):711-21. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90147-o. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8442770
-
Secretory phospholipase A2 enzymes in atherogenesis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Jun;16(3):341-4. doi: 10.1097/01.mol.0000169355.20395.55. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 15891396 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of secretory phospholipases in atherogenesis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2008 Jun;10(3):252-9. doi: 10.1007/s11883-008-0039-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2008. PMID: 18489854 Review.
-
Group V secretory phospholipase A2 is involved in macrophage activation and is sufficient for macrophage effector functions in allergic pulmonary inflammation.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 15;190(12):5927-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203202. Epub 2013 May 6. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23650617 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Phagocytosis in Macrophages by Membrane Ethanolamine Plasmalogens.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 24;9:1723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01723. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30087680 Free PMC article.
-
The cationic cluster of group IVA phospholipase A2 (Lys488/Lys541/Lys543/Lys544) is involved in translocation of the enzyme to phagosomes in human macrophages.J Lipid Res. 2010 Feb;51(2):388-99. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M001461. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19717620 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miRNAs: novel players in viral infection.Epigenomics. 2020 Feb;12(4):353-370. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0192. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Epigenomics. 2020. PMID: 32093516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhu K, Baudhuin LM, Hong G, Williams FS, Cristina KL, Kabarowski JHS, Witte ON, Xu Y. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41325–41335. - PubMed
-
- Clark JD, Lin LL, Kriz RW, Ramesha CS, Sultzman LA, Lin AY, Milona N, Knopf JL. Cell. 1991;65:1043–1051. - PubMed
-
- Pickard RT, Strifler BA, Kramer RM, Sharp JD. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8823–8831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

