Mitosis-specific promoter of the alfalfa cyclin-dependent kinase gene (Medsa;CDKB2;1) is activated by wounding and ethylene in a non-cell division-dependent manner
- PMID: 16407448
- PMCID: PMC1361335
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.105.072173
Mitosis-specific promoter of the alfalfa cyclin-dependent kinase gene (Medsa;CDKB2;1) is activated by wounding and ethylene in a non-cell division-dependent manner
Abstract
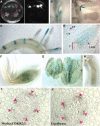
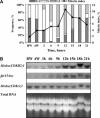
Cyclin-dependent serine/threonine kinases (CDKs) have pivotal roles in regulating the eukaryotic cell cycle. Plants possess a unique class of CDKs (B-type CDKs) with preferential protein accumulation at G2/M-phases; however, their exact functions are still enigmatic. Here we describe the functional characterization of a 360-bp promoter region of the alfalfa (Medicago sativa) CDKB2;1 gene in transgenic plants and cell lines. It is shown that the activity of the analyzed promoter was characteristic for proliferating meristematic regions in planta and specific for cells in the G2/M-phases in synchronized cell cultures. Immunohistochemical analysis of transgenic root sections further confirmed the correlation of the expression of the CDKB2;1 promoter-linked reporter genes with the accumulation of the correspondent kinase. It was found that, in addition to auxin (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) treatment, wounding could also induce both the reporter and endogenous genes in transgenic leaf explants. Furthermore, ethylene, known as a wound-response mediator, had a similar effect. The gene activation in response to wounding or ethephon was faster and occurred without the induction of cell cycle progression in contrast to the control auxin treatment. In silico analysis of this promoter indeed revealed the presence of a set of cis-elements, indicating not only cell cycle- but wound- and ethylene-dependent regulation of this CDK gene. Based on the presented data, we discuss the functional significance of the complex regulation of mitosis-specific CDK genes in plants.
Figures


References
-
- Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit ME (1992) Ethylene in Plant Biology, Ed 2. Academic Press, San Diego
-
- Ayaydin F, Vissi E, Mészáros T, Miskolczi P, Kovács I, Fehér A, Dombrádi V, Erdödi F, Gergely P, Dudits D (2000) Inhibition of serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatases causes premature activation of cdc2MsF kinase at G2/M transition and early mitotic microtubule organisation in alfalfa. Plant J 23: 85–96 - PubMed
-
- Barbulova A, Iantcheva A, Zhiponova M, Vlahova M, Atanassov A (2002. a) Establishment of embryogenic potential of economically important Bulgarian alfalfa cultivars (Medicago sativa L.). Biotechnol and Biotechnol Eq 16: 55–63
-
- Barbulova A, Iantcheva A, Zhiponova M, Vlahova M, Atanassov A (2002. b) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation for engineering of herbicide-resistance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Biotechnol and Biotechnol Eq 16: 21–27
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

