Inhibitors of differentiation and DNA binding (Ids) regulate Math1 and hair cell formation during the development of the organ of Corti
- PMID: 16407553
- PMCID: PMC6674393
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3859-05.2006
Inhibitors of differentiation and DNA binding (Ids) regulate Math1 and hair cell formation during the development of the organ of Corti
Abstract
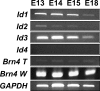
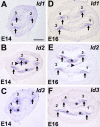
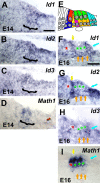
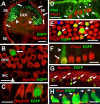
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor Math1 (also called Atoh1) is both necessary and sufficient for hair cell development in the mammalian cochlea (Bermingham et al., 1999; Zheng and Gao, 2000). Previous studies have demonstrated that a dynamic pattern of Math1 expression plays a key role in regulating the number and position of mechanosensory hair cells. However, the factors that regulate the temporal and spatial expression of Math1 within the cochlea are unknown. The bHLH-related inhibitors of differentiation and DNA binding (Id) proteins are known to negatively regulate many bHLH transcription factors, including Math1, in a number of different systems. Therefore, Id proteins are good candidates for regulating Math1 in the cochlea. Results from PCR and in situ hybridization indicate that Id1, Id2, and Id3 are expressed within the cochlear duct in a pattern that is consistent with a role in regulation of hair cell development. In particular, expression of Ids and Math1 overlapped in cochlear progenitor cells before cellular differentiation, but a specific downregulation of Id expression was observed in individual cells that differentiated as hair cells. In addition, progenitor cells in which the expression of Ids was maintained during the time period for hair cell differentiation were inhibited from developing as hair cells. These results indicate a key role for Ids in the regulation of expression of Math1 and hair cell differentiation in the developing cochlea.
Figures
References
-
- Andres-Barquin PJ, Hernandez MC, Israel MA (2000) Id genes in nervous system development. Histol Histopathol 15: 603–618. - PubMed
-
- Anniko M (1983) Cytodifferentiation of cochlear hair cells. Am J Otolaryngol 4: 375–388. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H (1990) The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 61: 49–59. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham NA, Hassan BA, Price SD, Vollrath MA, Ben-Arie N, Eatock RA, Bellen HJ, Lysakowski A, Zoghbi HY (1999) Math1: an essential gene for the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science 284: 1837–1841. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham-McDonogh O, Stone J, Hume C, Oesterle E (2005) Developmental expression of the homeobox transcription factor Prox1 in the murine organ of Corti. Assoc Res Otolaryngol Abstr 1353.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
