NMDA receptors in layer 4 spiny stellate cells of the mouse barrel cortex contain the NR2C subunit
- PMID: 16407568
- PMCID: PMC6674419
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4409-05.2006
NMDA receptors in layer 4 spiny stellate cells of the mouse barrel cortex contain the NR2C subunit
Abstract
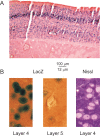
In layer 4 of the somatosensory cortex, the glutamatergic synapses that interconnect spiny stellate (SpS) neurons, which are the major targets of thalamocortical input, differ from most other neocortical excitatory synapses in that they have an extremely large NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-mediated component that is relatively insensitive to voltage-dependent Mg2+ blockade. We now report that this unique feature of the NMDA response reflects the distinctive subunit composition of the underlying receptors. We studied NMDAR-mediated miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs) and NMDA channel currents in tangential brain slices of mouse barrel cortex, which exclusively contain layer 4. NMDAR-mediated mEPSCs in SpS neurons were prominent at negative membrane potentials, and NMDA channels in outside-out patches excised from the somata of the same neurons had relatively low conductance and reduced susceptibility to Mg2+ block. These are characteristic features of heteromeric NMDAR assemblies that contain the NR2C subunit. Some patches also contained NMDA channels with higher conductance and a greater sensitivity to Mg2+. In the neocortex of transgenic mice in which a beta-galactosidase (lacZ) indicator gene was controlled by the NR2C promoter, the lacZ indicator was densely expressed in layer 4. In current-clamp recordings, blockade of NMDARs caused hyperpolarization and an increase in apparent input resistance. Our data demonstrate that the SpS neurons of layer 4 functionally express NR2C subunits; this is the likely explanation for their ability to generate large NMDAR-mediated EPSPs that are effective at resting potential, without previous depolarization.
Figures


References
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, Yasuda H, von Zastrow M, Malenka RC (2000) Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat Neurosci 3: 1291-1300. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361: 31-39. - PubMed
-
- Brusa R, Zimmermann F, Koh DS, Feldmeyer D, Gass P, Seeburg PH, Sprengel R (1995) Early-onset epilepsy and postnatal lethality associated with an editing-deficient GluR-B allele in mice. Science 270: 1677-1680. - PubMed
-
- Carson F (1990) Histotechnology: a self-instructional text, Ed 1. Chicago: ASCP.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
