The elucidation of novel SH2 binding sites on PLD2
- PMID: 16407827
- PMCID: PMC3074567
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209340
The elucidation of novel SH2 binding sites on PLD2
Abstract
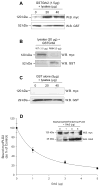
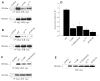
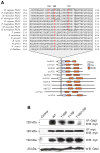
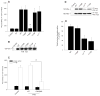
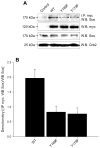
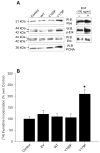
Our laboratory has recently reported that the enzyme phospholipase D2 (PLD2) exists as a ternary complex with PTP1b and the growth factor receptor bound protein 2 (Grb2). Here, we establish the mechanistic underpinnings of the PLD2/Grb2 association. We have identified residues Y(169) and Y(179) in the PLD2 protein as being essential for the Grb2 interaction. We present evidence indicating that Y(169) and Y(179) are located within two consensus sites in PLD2 that mediate an SH2 interaction with Grb2. This was demonstrated with an SH2-deficient GSTGrb2 R86K mutant that failed to pull-down PLD2 in vitro. In order to elucidate the functions of the two neighboring tyrosines, we created a new class of deletion and point mutants in PLD2. Phenylalanine replacement of Y(169) (PLD2 Y169F) or Y(179) (PLD2 Y179F) reduced Grb2 binding while simultaneous mutation completely abolished it. The role of the two binding sites on PLD2 was found to be functionally nonequivalent: Y(169) serves to modulate the activity of the enzyme, whereas Y(179) regulates total tyrosine phosphorylation of the protein. Interestingly, binding of Grb2 to PLD2 occurs irrespectively of lipase activity, since Grb2 binds to catalytically inactive PLD2 mutants. Finally, PLD2 residues Y(169) and Y(179) are necessary for the recruitment of Sos, but only overexpression of the PLD2 Y179F mutant resulted in increased Ras activity, p44/42(Erk) phosphorylation and enhanced DNA synthesis. Since Y(169) remains able to modulate enzyme activity and is capable of binding to Grb2 in the PLD2 Y179F mutant, we propose that Y(169) is kept under negative regulation by Y(179). When this is released, Y(169) mediates cellular proliferation through the Ras/MAPK pathway.
Figures

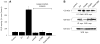
Similar articles
-
The Grb2/PLD2 interaction is essential for lipase activity, intracellular localization and signaling in response to EGF.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 30;367(3):814-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.021. Epub 2007 Jan 12. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17276458 Free PMC article.
-
PLD2 has both enzymatic and cell proliferation-inducing capabilities, that are differentially regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Nov 13;389(2):224-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.109. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19715678 Free PMC article.
-
The exquisite regulation of PLD2 by a wealth of interacting proteins: S6K, Grb2, Sos, WASp and Rac2 (and a surprise discovery: PLD2 is a GEF).Cell Signal. 2011 Dec;23(12):1885-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.06.017. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21740967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis of phospholipase D2-induced chemotaxis: elucidation of differential pathways in macrophages and fibroblasts.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;30(18):4492-506. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00229-10. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20647543 Free PMC article.
-
New concepts in phospholipase D signaling in inflammation and cancer.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Jul 7;10:1356-69. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.116. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20623096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Antithrombotic Strategy by Targeting Phospholipase D in Human Platelets.J Clin Med. 2018 Nov 14;7(11):440. doi: 10.3390/jcm7110440. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30441821 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D: enzymology, functionality, and chemical modulation.Chem Rev. 2011 Oct 12;111(10):6064-119. doi: 10.1021/cr200296t. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 21936578 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Role of phospholipase d in g-protein coupled receptor function.Membranes (Basel). 2014 Jul 3;4(3):302-18. doi: 10.3390/membranes4030302. Membranes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24995811 Free PMC article.
-
A novel phospholipase D2-Grb2-WASp heterotrimer regulates leukocyte phagocytosis in a two-step mechanism.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;31(22):4524-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05684-11. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21930784 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian phospholipase D: Function, and therapeutics.Prog Lipid Res. 2020 Apr;78:101018. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2019.101018. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 31830503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banno Y, Ohguchi K, Matsumoto N, Koda M, Ueda M, Hara A, Dikic I, Nozawa Y. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:16319–24. - PubMed
-
- Bourgoin S, Grinstein S. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:11908–11916. - PubMed
-
- Chardin P, Camonis JH, Gale NW, van Aelst L, Schlessinger J, Wigler MH, Bar-Sagi D. Science. 1993;260:1338–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

