Processive movement of single kinesins on crowded microtubules visualized using quantum dots
- PMID: 16407972
- PMCID: PMC1383520
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600937
Processive movement of single kinesins on crowded microtubules visualized using quantum dots
Abstract
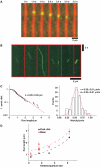
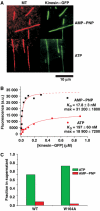
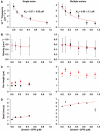
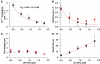
Kinesin-1 is a processive molecular motor transporting cargo along microtubules. Inside cells, several motors and microtubule-associated proteins compete for binding to microtubules. Therefore, the question arises how processive movement of kinesin-1 is affected by crowding on the microtubule. Here we use total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy to image in vitro the runs of single quantum dot-labelled kinesins on crowded microtubules under steady-state conditions and to measure the degree of crowding on a microtubule at steady-state. We find that the runs of kinesins are little affected by high kinesin densities on a microtubule. However, the presence of high densities of a mutant kinesin that is not able to step efficiently reduces the average speed of wild-type kinesin, while hardly changing its processivity. This indicates that kinesin waits in a strongly bound state on the microtubule when encountering an obstacle until the obstacle unbinds and frees the binding site for kinesin's next step. A simple kinetic model can explain quantitatively the behaviour of kinesin under both crowding conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Arnal I, Wade RH (1998) Nucleotide-dependent conformations of the kinesin dimer interacting with microtubules. Structure 6: 33–38 - PubMed
-
- Block SM, Goldstein LS, Schnapp BJ (1990) Bead movement by single kinesin molecules studied with optical tweezers. Nature 348: 348–352 - PubMed
-
- Castoldi M, Popov AV (2003) Purification of brain tubulin through two cycles of polymerization–depolymerization in a high-molarity buffer. Protein Expr Purif 32: 83–88 - PubMed
-
- Chan WC, Maxwell DJ, Gao X, Bailey RE, Han M, Nie S (2002) Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13: 40–46 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

