Escherichia coli O157 outbreak associated with fresh unpasteurized goats' cheese
- PMID: 16409661
- PMCID: PMC2870372
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268805004887
Escherichia coli O157 outbreak associated with fresh unpasteurized goats' cheese
Abstract
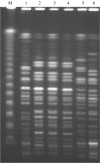
A family cluster of three cases of Escherichia coli O157 infection was identified in France. Two cases developed haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. The source was fresh unpasteurized goats' cheese, produced by an independent producer. Three E. coli O157 strains, isolated from one HUS case and faeces of one cow and one goat, were indistinguishable by toxin type and PFGE pattern.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shopper cards data and storage practices for the investigation of an outbreak of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli O157 infections.Med Mal Infect. 2013 Sep;43(9):368-73. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Med Mal Infect. 2013. PMID: 23910937
-
Desperately seeking diarrhoea: outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome caused by emerging sorbitol-fermenting shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H-, Germany, 2009.Zoonoses Public Health. 2011 Dec;58(8):567-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2011.01405.x. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Zoonoses Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21824358
-
Community-wide outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with consumption of frozen beef burgers.Epidemiol Infect. 2009 Jun;137(6):889-96. doi: 10.1017/S0950268808001490. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Epidemiol Infect. 2009. PMID: 18945376
-
[Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection].Recenti Prog Med. 1999 Nov;90(11):613-8. Recenti Prog Med. 1999. PMID: 10608152 Review. Italian.
-
[Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and its infection: from 1977 to 1995].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Mar;55(3):635-40. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9086772 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Shiga toxin (stx) encoding genes in sheep and goats reared in Trinidad and Tobago.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 15;17(11):e0277564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277564. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36378686 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological and Physico-Chemical Changes During Manufacture of an Italian Goat Cheese Made from Raw Milk.Ital J Food Saf. 2014 Dec 18;3(4):4586. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2014.4586. eCollection 2014 Dec 9. Ital J Food Saf. 2014. PMID: 27800372 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Essential Oils on Escherichia coli Inactivation in Cheese as Described by Meta-Regression Modelling.Foods. 2020 Jun 2;9(6):716. doi: 10.3390/foods9060716. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32498276 Free PMC article.
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome in pediatric intensive care units in são paulo, Brazil.Open Microbiol J. 2011;5:76-82. doi: 10.2174/1874285801105010076. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Open Microbiol J. 2011. PMID: 21804902 Free PMC article.
-
Spread of E. coli O157 infection among Scottish cattle farms: stochastic models and model selection.Epidemics. 2010 Mar;2(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2010.02.001. Epidemics. 2010. PMID: 20640032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griffin PM, Tauxe AV. The epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7, other enterohemorragic E. coli and the associated haemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:60–98. - PubMed
-
- Tarr PI. Escherichia coli O157:H7: clinical, diagnostic, and epidemiological aspects of human infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Haeghebaert S, Vaillant V, Bouvet P, Grimont F.and the Paediatric Nephrologists network. Surveillance of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in children under 15 years of age in France in 2000. BEH (serial online) (http://www.invs.sante.fr/beh/2002/29/beh_29_2002.pdf). Accessed 19 August 2004
-
- Read SC, Clarke RC, Martin A et al. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from animals and food sources. Mol Cell Probes. 1992;6:153–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical