Cytokeratin 8/18 expression indicates a poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity
- PMID: 16412231
- PMCID: PMC1379654
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-10
Cytokeratin 8/18 expression indicates a poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity
Abstract
Background: Intermediary filaments are involved in cell motility and cancer progression. In a variety of organs, the expression of distinct intermediary filaments are associated with patient prognosis. In this study, we seeked to define the prognostic potential of cytokeratin and vimentin expression patterns in squamous cell carcinomas (SCC's) of the oral cavity.
Methods: 308 patients with histologically proven and surgically treated squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity were investigated for the immunohistochemical expression of a variety of intermediary filaments including high- and low-molecular weight cytokeratins (Ck's), such as Ck 5/6, Ck 8/18, Ck 1, CK 10, Ck 14, Ck 19 and vimentin, using the tissue microarray technique. Correlations between clinical features and the expression of Cytokeratins and vimentin were evaluated statistically by Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariate Cox regression analysis.
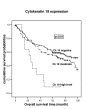
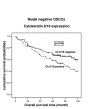
Results: The expression of Ck 8/18 and Ck 19 were overall significantly correlated with a poor clinical prognosis (Ck 8/18 p = 0.04; Ck19 p < 0.01). These findings could also be reproduced for Ck 8/18 in primary nodal-negative SCC's and held true in multivariate-analysis. No significant correlation with patient prognosis could be found for the expression of the other cytokeratins and for vimentin.
Conclusion: The expression of Ck 8/18 in SCC's of the oral cavity is an independent prognostic marker and indicates a decreased overall and progression free survival. These results provide an extended knowledge about the role of intermediary filament expression patterns in SCC's.
Figures


References
-
- Presland RB, Jurevic RJ. Making sense of the epithelial barrier: what molecular biology and genetics tell us about the functions of oral mucosal and epidermal tissues. J Dent Educ. 2002;66:564–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

