A genetic system for rhesus monkey rhadinovirus: use of recombinant virus to quantitate antibody-mediated neutralization
- PMID: 16415030
- PMCID: PMC1346924
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.3.1549-1562.2006
A genetic system for rhesus monkey rhadinovirus: use of recombinant virus to quantitate antibody-mediated neutralization
Abstract
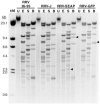
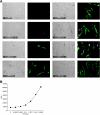
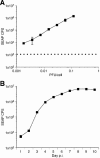
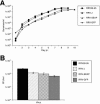
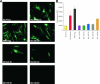
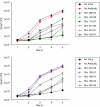
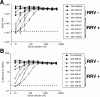
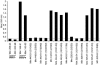
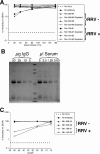
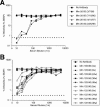
Rhesus monkey rhadinovirus (RRV), a simian gamma-2 herpesvirus closely related to the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, replicates lytically in cultured rhesus monkey fibroblasts and establishes persistence in B cells. Overlapping cosmid clones were generated that encompass the entire 130-kilobase-pair genome of RRV strain 26-95, including the terminal repeat regions required for its replication. Cloned RRV that was produced by cotransfection of overlapping cosmids spanning the entire RRV26-95 genome replicated with growth kinetics and to titers similar to those of the parental, uncloned, wild-type RRV26-95. Expression cassettes for secreted-engineered alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) were inserted upstream of the R1 gene, and the cosmid-based system for RRV genome reconstitution was used to generate replication-competent, recombinant RRV that expressed either the SEAP or GFP reporter gene. Using the SEAP and GFP recombinant RRVs, assays were developed to monitor RRV infection, neutralization, and replication. Heat-inactivated sera from rhesus monkeys that were naturally or experimentally infected with RRV were assayed for their ability to neutralize RRV-SEAP and RRV-GFP infectivity using rhesus monkey fibroblasts. Sera from RRV-positive monkeys, but not RRV-negative monkeys, were consistently able to neutralize RRV infectivity when assayed by the production of SEAP activity or by the ability to express GFP. The neutralizing activity was present in the immunoglobulin fraction. Of the 17 rhesus monkeys tested, sera from rhesus monkey 26-95, i.e., the monkey that yielded the RRV 26-95 isolate, had the highest titer of neutralizing activity against RRV26-95. This cosmid-based genetic system and the reporter virus neutralization assay will facilitate study of the contribution of individual RRV glycoproteins to entry into different cell types, particularly fibroblasts and B cells.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander, L., L. Denekamp, A. Knapp, M. R. Auerbach, B. Damania, and R. C. Desrosiers. 2000. The primary sequence of rhesus monkey rhadinovirus isolate 26-95: sequence similarities to Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and rhesus monkey rhadinovirus isolate 17577. J. Virol. 74:3388-3398. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, Y., E. Cesarman, M. S. Pessin, F. Lee, J. Culpepper, D. M. Knowles, and P. S. Moore. 1994. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science 266:1865-1869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

