A gammaherpesvirus 68 gene 50 null mutant establishes long-term latency in the lung but fails to vaccinate against a wild-type virus challenge
- PMID: 16415035
- PMCID: PMC1346930
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.3.1592-1598.2006
A gammaherpesvirus 68 gene 50 null mutant establishes long-term latency in the lung but fails to vaccinate against a wild-type virus challenge
Abstract
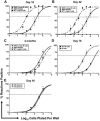
The gammaherpesvirus immediate-early genes are critical regulators of virus replication and reactivation from latency. Rta, encoded by gene 50, serves as the major transactivator of the lytic program and is highly conserved among all the gammaherpesviruses, including Epstein-Barr virus, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, and murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (gammaHV68). Introduction of a translation stop codon in gammaHV68 gene 50 (gene 50.stop gammaHV68) demonstrated that Rta is essential for virus replication in vitro. To investigate the role that virus replication plays in the establishment and maintenance of latency, we infected mice with gene 50.stop gammaHV68. Notably, the gene 50.stop virus established a long-term infection in lung B cells following intranasal infection of mice but was unable to establish latency in the spleen. This complete block in the establishment of latency in the spleen was also seen when lytic virus production was inhibited by treating mice infected with wild-type virus with the antiviral drug cidofovir, implicating virus replication and not an independent function of Rta in the establishment of splenic latency. Furthermore, we showed that gene 50.stop gammaHV68 was unable to prime the immune system and was unable to protect against a challenge with wild-type gammaHV68, despite its ability to chronically infect lung B cells. These data indicate gammaherpesviruses that are unable to undergo lytic replication in vivo may not be viable vaccine candidates despite the detection of cells harboring viral genome at late times postinfection.
Figures
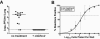

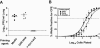
Similar articles
-
Establishment and maintenance of long-term murine gammaherpesvirus 68 latency in B cells in the absence of CD40.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(5):2891-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.5.2891-2899.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15709008 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 Expressing Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency-Associated Nuclear Antigen (LANA) Reveals both Functional Conservation and Divergence in LANA Homologs.J Virol. 2017 Sep 12;91(19):e00992-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00992-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28747501 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF48 Is an RTA-Responsive Gene Product and Functions in both Viral Lytic Replication and Latency during In Vivo Infection.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(11):5788-800. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00406-15. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25762743 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon blocks gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency in a cell type-specific manner.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):6134-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00108-07. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17360749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-guided gene editing of the murine gammaherpesvirus 68 genome reduces infectious virus production.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 4;16(6):e0252313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252313. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34086743 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of TLR9 immunostimulatory motifs in the genome of a gammaherpesvirus.J Immunol. 2011 Jul 15;187(2):887-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003737. Epub 2011 Jun 10. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21666062 Free PMC article.
-
Viral FGARAT ORF75A promotes early events in lytic infection and gammaherpesvirus pathogenesis in mice.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Feb 1;14(2):e1006843. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006843. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29390024 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 LANA and SOX Homologs Counteract ATM-Driven p53 Activity during Lytic Viral Replication.J Virol. 2015 Dec 16;90(5):2571-85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02867-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26676792 Free PMC article.
-
A replication-deficient gammaherpesvirus vaccine protects mice from lytic disease and reduces latency establishment.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Jun 24;9(1):116. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00908-x. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38914546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Espinoza, J. C., and J. Kuznar. 2002. Rapid simultaneous detection and quantitation of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV). J. Virol. Methods 105:81-85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

