Searching for the molecular arrangement of transmembrane ceramide channels
- PMID: 16415050
- PMCID: PMC1403165
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.071977
Searching for the molecular arrangement of transmembrane ceramide channels
Abstract
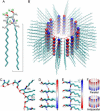
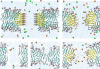
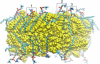
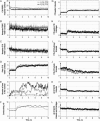
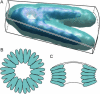
Ceramides have been implicated in the initiation of apoptosis by permeabilizing the mitochondrial outer membrane to small proteins, including cytochrome c. In addition, ceramides were shown to form large metastable channels in planar membranes and liposomes, indicating that these lipids permeabilize membranes directly. Here we analyze molecular models of ceramide channels and test their stability in molecular dynamics simulations. The structural units are columns of four to six ceramides H-bonded via amide groups and arranged as staves in either a parallel or antiparallel manner. Two cylindrical assemblies of 14 columns (four or six molecules per column) were embedded in a fully hydrated palmitoyloleoyl-phosphatidylcholine phospholipid bilayer, and simulated for 24 ns in total. After equilibration, the water-filled pore adopted an hourglass-like shape as headgroups of ceramides and phospholipids formed a smooth continuous interface. The structure-stabilizing interactions were both hydrogen bonds between the headgroups (including water-mediated interactions) and packing of the hydrocarbon tails. Ceramide's essential double bond reduced the mobility of the hydrocarbon tails and stabilized their packing. The six-column assembly remained stable throughout a 10-ns simulation. During simulations of four-column assemblies, pairs of columns displayed the tendency of splitting out from the channels, consistent with the previously proposed mechanism of channel disassembly.
Figures


References
-
- Montes, L. R., M. B. Ruiz-Arguello, F. M. Goni, and A. Alonso. 2002. Membrane restructuring via ceramide results in enhanced solute efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 277:11788–11794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

