Genome-scale identification of membrane-associated human mRNAs
- PMID: 16415983
- PMCID: PMC1326219
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020011
Genome-scale identification of membrane-associated human mRNAs
Abstract
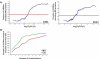
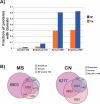
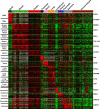
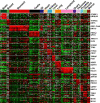
The subcellular localization of proteins is critical to their biological roles. Moreover, whether a protein is membrane-bound, secreted, or intracellular affects the usefulness of, and the strategies for, using a protein as a diagnostic marker or a target for therapy. We employed a rapid and efficient experimental approach to classify thousands of human gene products as either "membrane-associated/secreted" (MS) or "cytosolic/nuclear" (CN). Using subcellular fractionation methods, we separated mRNAs associated with membranes from those associated with the soluble cytosolic fraction and analyzed these two pools by comparative hybridization to DNA microarrays. Analysis of 11 different human cell lines, representing lymphoid, myeloid, breast, ovarian, hepatic, colon, and prostate tissues, identified more than 5,000 previously uncharacterized MS and more than 6,400 putative CN genes at high confidence levels. The experimentally determined localizations correlated well with in silico predictions of signal peptides and transmembrane domains, but also significantly increased the number of human genes that could be cataloged as encoding either MS or CN proteins. Using gene expression data from a variety of primary human malignancies and normal tissues, we rationally identified hundreds of MS gene products that are significantly overexpressed in tumors compared to normal tissues and thus represent candidates for serum diagnostic tests or monoclonal antibody-based therapies. Finally, we used the catalog of CN gene products to generate sets of candidate markers of organ-specific tissue injury. The large-scale annotation of subcellular localization reported here will serve as a reference database and will aid in the rational design of diagnostic tests and molecular therapies for diverse diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Brekke OH, Sandlie I. Therapeutic antibodies for human diseases at the dawn of the twenty-first century. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:52–62. - PubMed
-
- Sturgeon C. Practice guidelines for tumor marker use in the clinic. Clin Chem. 2002;48:1151–1159. - PubMed
-
- Fischbach FT. A manual of laboratory and diagnostic test. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2003. 1312. p.
-
- Tashiro K, Tada H, Heilker R, Shirozu M, Nakano T, et al. Signal sequence trap: A cloning strategy for secreted proteins and type I membrane proteins. Science. 1993;261:600–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

