Major phosphorylation of SF1 on adjacent Ser-Pro motifs enhances interaction with U2AF65
- PMID: 16420481
- PMCID: PMC1949809
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05091.x
Major phosphorylation of SF1 on adjacent Ser-Pro motifs enhances interaction with U2AF65
Abstract
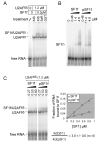
Protein phosphorylation ensures the accurate and controlled expression of the genome, for instance by regulating the activities of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Here we report that splicing factor 1 (SF1), which is involved in an early step of intronic sequence recognition, is highly phosphorylated in mammalian cells on two serines within an SPSP motif at the junction between its U2AF65 and RNA binding domains. We show that SF1 interacts in vitro with the protein kinase KIS, which possesses a 'U2AF homology motif' (UHM) domain. The UHM domain of KIS is required for KIS and SF1 to interact, and for KIS to efficiently phosphorylate SF1 on the SPSP motif. Importantly, SPSP phosphorylation by KIS increases binding of SF1 to U2AF65, and enhances formation of the ternary SF1-U2AF65-RNA complex. These results further suggest that this phosphorylation event has an important role for the function of SF1, and possibly for the structural rearrangements associated with spliceosome assembly and function.
Figures
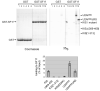
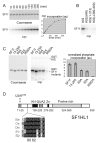
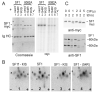
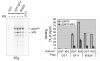
References
-
- Brow DA. Allosteric cascade of spliceosome activation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002;36:333–360. - PubMed
-
- Tazi J, Kornstadt U, Rossi F, Jeanteur P, Cathala G, Brunel C, Luhrmann R. Thiophosphorylation of U1-70K protein inhibits pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1993;363:283–286. - PubMed
-
- Stojdl DF, Bell JC. SR protein kinases: the splice of life. Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;77:293–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

