Function-blocking antithrombospondin-1 monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 16420580
- PMCID: PMC2219891
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01723.x
Function-blocking antithrombospondin-1 monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
Background: Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) has been implicated in many different processes based in part on inhibitory activities of anti-TSP-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
Objective: To map epitopes of 13 anti-TSP-1 mAbs to individual modules or groups of modules spanning TSP-1 and the closely related TSP-2 homolog.
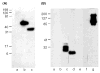
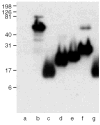
Results: The mapping has led to assignment or reassignment of the epitopes of four mAbs, refinement of the epitopes of six mAbs, and confirmation of the epitopes of the remaining three mAbs. ESTs10, P12, and MA-II map to the N-terminal domain; 5G11, TSP127.6, and ESTs12 to the third properdin module; C6.7, HB8432, and P10 to epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like modules 1 and/or 2; and A6.1, mAb133, MA-I, and D4.6 to the calcium-binding wire module. A6.1, which recognizes a region of the wire that is identical in mouse and human TSP-1, reacts with TSP-1 from both species, and also reacts weakly with human TSP-2. Two other mouse antihuman TSP-1 mAbs, A4.1 and D4.6, also react with mouse TSP-1.
Conclusions: Consideration of previous literature and mapping of epitopes of inhibitory mAbs suggest that biological activities are present throughout TSP-1, including the EGF-like modules that have not been implicated in the past. Because the epitopes for 10 of the antibodies likely are within 18 nm of one another in calcium-replete TSP-1, some of the inhibitory effects may result from steric hindrance. Such seems to be the case for mAb133, which binds the calcium-binding wire but is still able to interfere with the activation of latent TGF-beta by the properdin modules.
Figures


References
-
- Adams JC. Thrombospondins: multifunctional regulators of cell interactions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:25–51. - PubMed
-
- Mosher DF, Huwiler KG, Misenheimer TM, Annis DS. Expression of recombinant matrix components using baculoviruses. Methods Cell Biol. 2002;69:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Calzada MJ, Annis DS, Zeng B, Marcinkiewicz C, Banas B, Lawler J, Mosher DF, Roberts DD. Identification of novel beta-1 integrin binding sites in the type 1 and type 2 repeats of thrombospondin-1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41734–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

