In vivo imaging of preferential motor axon outgrowth to and synaptogenesis at prepatterned acetylcholine receptor clusters in embryonic zebrafish skeletal muscle
- PMID: 16421313
- PMCID: PMC6675385
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3656-05.2006
In vivo imaging of preferential motor axon outgrowth to and synaptogenesis at prepatterned acetylcholine receptor clusters in embryonic zebrafish skeletal muscle
Abstract
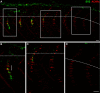
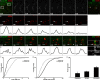
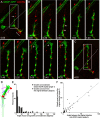
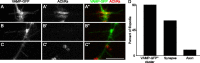
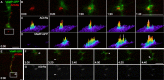
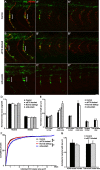
Little is known about the spatial and temporal dynamics of presynaptic and postsynaptic specializations that culminate in synaptogenesis. Here, we imaged presynaptic vesicle clusters in motor axons and postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clusters in embryonic zebrafish to study the earliest events in synaptogenesis in vivo. Prepatterned AChR clusters are present on muscle fibers in advance of motor axon outgrowth from the spinal cord. Motor axon growth cones and filopodia are selectively extended toward and contact prepatterned AChR clusters, followed by the rapid clustering of presynaptic vesicles and insertion of additional AChRs, hallmarks of synaptogenesis. All initially formed neuromuscular synapses contain AChRs that were inserted into the membrane at the time the prepattern is present. Examination of embryos in which AChRs were blocked or clustering is absent showed that neither receptor activity or receptor protein is required for these events to occur. Thus, during initial synaptogenesis, postsynaptic differentiation precedes presynaptic differentiation, and prepatterned neurotransmitter clusters mark sites destined for synapse formation.
Figures


References
-
- Apel ED, Glass DJ, Moscoso LM, Yancopoulos GD, Sanes JR (1997) Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron 18: 623–635. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Burden SJ, Harris AJ (2002) Patterning of skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12: 100–103. - PubMed
-
- Bloch RJ (1988) Molecular events in synaptogenesis: nerve-muscle adhesion and postsynaptic differentiation. Am J Physiol 254: C345–C364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
