A multifunctional cytoprotective agent that reduces neurodegeneration after ischemia
- PMID: 16423893
- PMCID: PMC1360591
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510573103
A multifunctional cytoprotective agent that reduces neurodegeneration after ischemia
Abstract
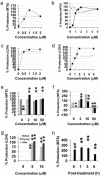
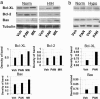
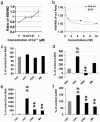
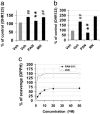
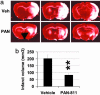
Cellular and molecular pathways underlying ischemic neurotoxicity are multifaceted and complex. Although many potentially neuroprotective agents have been investigated, the simplicity of their protective mechanisms has often resulted in insufficient clinical utility. We describe a previously uncharacterized class of potent neuroprotective compounds, represented by PAN-811, that effectively block both ischemic and hypoxic neurotoxicity. PAN-811 disrupts neurotoxic pathways by at least two modes of action. It causes a reduction of intracellular-free calcium as well as free radical scavenging resulting in a significant decrease in necrotic and apoptotic cell death. In a rat model of ischemic stroke, administration of PAN-811 i.c.v. 1 h after middle cerebral artery occlusion resulted in a 59% reduction in the volume of infarction. Human trials of PAN-811 for an unrelated indication have established a favorable safety and pharmacodynamic profile within the dose range required for neuroprotection warranting its clinical trial as a neuroprotective drug.
Figures
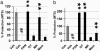
References
-
- Zerwic, J. J., Ennen, K. & DeVon, H. A. (2002) AAOHN J. 50, 354-359. - PubMed
-
- Liu, S., Shi, H., Liu, W., Furuichi, T., Timmins, G. S. & Liu, K. J. (2004) J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 24, 343-349. - PubMed
-
- MacGregor, D. G., Avshalumov, M. V. & Rice, M. E. (2003) J. Neurochem. 85, 1402-1411. - PubMed
-
- Kristian, T., Gido, G., Kuroda, S., Schutz, A. & Siesjo, B. K. (1998) Exp. Brain Res. 120, 503-509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

