RuvAB is essential for replication forks reversal in certain replication mutants
- PMID: 16424908
- PMCID: PMC1383526
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600941
RuvAB is essential for replication forks reversal in certain replication mutants
Abstract
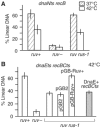
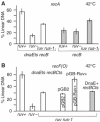
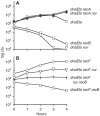
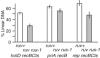
Inactivated replication forks may be reversed by the annealing of leading- and lagging-strand ends, resulting in the formation of a Holliday junction (HJ) adjacent to a DNA double-strand end. In Escherichia coli mutants deficient for double-strand end processing, resolution of the HJ by RuvABC leads to fork breakage, a reaction that we can directly quantify. Here we used the HJ-specific resolvase RusA to test a putative role of the RuvAB helicase in replication fork reversal (RFR). We show that the RuvAB complex is required for the formation of a RusA substrate in the polymerase III mutants dnaEts and holD, affected for the Pol III catalytic subunit and clamp loader, and in the helicase mutant rep. This finding reveals that the recombination enzyme RuvAB targets forks in vivo and we propose that it directly converts forks into HJs. In contrast, RFR occurs in the absence of RuvAB in the dnaNts mutant, affected for the processivity clamp of Pol III, and in the priA mutant, defective for replication restart. This suggests alternative pathways of RFR.
Figures

References
-
- Benson FE, West SC (1994) Substrate specificity of the Escherichia coli ruvc protein—resolution of three- and four-stranded recombination intermediates. J Biol Chem 269: 5195–5201 - PubMed
-
- Bolt EL, Lloyd RG (2002) Substrate specificity of RusA resolvase reveals the DNA structures targeted by RuvAB and RecG in vivo. Mol Cell 10: 187–198 - PubMed
-
- Carr AM (2002) Checking that replication breakdown is not terminal. Science 297: 557–558 - PubMed
-
- Chan SN, Harris L, Bolt EL, Whitby MC, Lloyd RG (1997) Sequence specificity and biochemical characterization of the RusA Holliday junction resolvase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 272: 14873–14882 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

