The influence of the pituitary tumor transforming gene-1 (PTTG-1) on survival of patients with small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 16426442
- PMCID: PMC1360069
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3163-5-4
The influence of the pituitary tumor transforming gene-1 (PTTG-1) on survival of patients with small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: PTTG-1 (pituitary tumor transforming gene) is a novel oncogene that is overexpressed in tumors, such as pituitary adenoma, breast and gastrointestinal cancers as well as in leukemia. In this study, we examined the role of PTTG-1 expression in lung cancer with regard to histological subtype, the correlation of PTTG-1 to clinical parameters and relation on patients' survival.
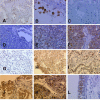
Methods: Expression of PTTG-1 was examined immunohistochemically on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections of 136 patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and 91 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), retrospectively. The intensity of PTTG-1 expression as well as the proportion of PTTG-1 positive cells within a tumor was used for univariate and multivariate analysis.
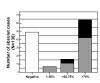
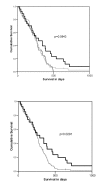
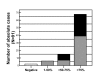
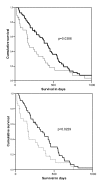
Results: PTTG-1 expression was observed in 64% of SCLC tumors and in 97.8% of NSCLC tumors. In patients with SCLC, negative or low PTTG-1 expression was associated with a shorter mean survival time compared with patients with strong PTTG-1 expression (265 +/- 18 days vs. 379 +/- 66 days; p = 0.0291). Using the Cox regression model for multivariate analysis, PTTG-1 expression was a significant predictor for survival next to performance status, tumor stage, LDH and hemoglobin. In contrast, in patients with NSCLC an inverse correlation between survival and PTTG-1 expression was seen. Strong PTTG-1 expression was associated with a shorter mean survival of 306 +/- 58 days compared with 463 +/- 55 days for those patients with no or low PTTG-1 intensities (p = 0.0386). Further, PTTG-1 expression was associated with a more aggressive NSCLC phenotype with an advanced pathological stage, extensive lymph node metastases, distant metastases and increased LDH level. Multivariate analysis using Cox regression confirmed the prognostic relevance of PTTG-1 expression next to performance status and tumor stage in patients with NSCLC.
Conclusion: Lung cancers belong to the group of tumors expressing PTTG-1. Dependent on the histological subtype of lung cancer, PTTG-1 expression was associated with a better outcome in patients with SCLC and a rather unfavourable outcome for patients with NSCLCs. These results may reflect the varying role of PTTG-1 in the pathophysiology of the different histological subtypes of lung cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Hosoe S, Ueno K, Shigedo Y, Tachibana I, Osaki T, Kumagai T, Tanio Y, Kawase I, Nakamura Y, Kishimoto T. A frequent deletion of chromosime 5q21 in advanced small cell and non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Research. 1994;54:1787–1790. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Hsu TC, Annegers JF, Amos CI, Fueger JJ, Spitz MR. A case-control study of nonrandom distribution of bleomycin-induced chromatid breaks in lymphocytes of lung cancer cases. Cancer Research. 1995;55:557–561. - PubMed
-
- Hosoe S. Search for the tumor-suppressor gene(s) on chromosome 5q. which may play an important role for the progression of lung cancer. Nippon Rinsho-Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine. 1996;54:482–486. - PubMed
-
- Shibata Y, Haruki N, Kuwabara Y, Nishiwaki 'T, Kato J, Shinoda N, Sato A, Kimura M, Koyama H, Toyama T, Ishiguro H, Kudo J, Terashita Y, Konishi S, Fujii Y. Expression of PTTG (Pituitary Tumor Transforming Gene) in esophageal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32:233–7. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyf058. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

