Allosteric signaling of ATP hydrolysis in GroEL-GroES complexes
- PMID: 16429154
- PMCID: PMC2871290
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1046
Allosteric signaling of ATP hydrolysis in GroEL-GroES complexes
Abstract
The double-ring chaperonin GroEL and its lid-like cochaperonin GroES form asymmetric complexes that, in the ATP-bound state, mediate productive folding in a hydrophilic, GroES-encapsulated chamber, the so-called cis cavity. Upon ATP hydrolysis within the cis ring, the asymmetric complex becomes able to accept non-native polypeptides and ATP in the open, trans ring. Here we have examined the structural basis for this allosteric switch in activity by cryo-EM and single-particle image processing. ATP hydrolysis does not change the conformation of the cis ring, but its effects are transmitted through an inter-ring contact and cause domain rotations in the mobile trans ring. These rigid-body movements in the trans ring lead to disruption of its intra-ring contacts, expansion of the entire ring and opening of both the nucleotide pocket and the substrate-binding domains, admitting ATP and new substrate protein.
Figures
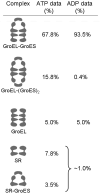



References
-
- Sigler PB, et al. Structure and function in GroEL-mediated protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;67:581–608. - PubMed
-
- Saibil HR, Ranson NA. The chaperonin folding machine. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:627–632. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl FU. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science. 2002;295:1852–1858. - PubMed
-
- Fenton WA, Horwich AL. Chaperone-mediated protein folding: fate of substrate polypeptide. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2003;36:229–256. - PubMed
-
- Yifrach O, Horovitz A. Two lines of allosteric communication in the oligomeric chaperonin GroEL are revealed by the single mutation Arg196->Ala. J. Mol. Biol. 1994;243:397–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

