Accurate prediction of the functional significance of single nucleotide polymorphisms and mutations in the ABCA1 gene
- PMID: 16429166
- PMCID: PMC1342637
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010083
Accurate prediction of the functional significance of single nucleotide polymorphisms and mutations in the ABCA1 gene
Abstract
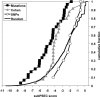
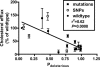
The human genome contains an estimated 100,000 to 300,000 DNA variants that alter an amino acid in an encoded protein. However, our ability to predict which of these variants are functionally significant is limited. We used a bioinformatics approach to define the functional significance of genetic variation in the ABCA1 gene, a cholesterol transporter crucial for the metabolism of high density lipoprotein cholesterol. To predict the functional consequence of each coding single nucleotide polymorphism and mutation in this gene, we calculated a substitution position-specific evolutionary conservation score for each variant, which considers site-specific variation among evolutionarily related proteins. To test the bioinformatics predictions experimentally, we evaluated the biochemical consequence of these sequence variants by examining the ability of cell lines stably transfected with the ABCA1 alleles to elicit cholesterol efflux. Our bioinformatics approach correctly predicted the functional impact of greater than 94% of the naturally occurring variants we assessed. The bioinformatics predictions were significantly correlated with the degree of functional impairment of ABCA1 mutations (r2 = 0.62, p = 0.0008). These results have allowed us to define the impact of genetic variation on ABCA1 function and to suggest that the in silico evolutionary approach we used may be a useful tool in general for predicting the effects of DNA variation on gene function. In addition, our data suggest that considering patterns of positive selection, along with patterns of negative selection such as evolutionary conservation, may improve our ability to predict the functional effects of amino acid variation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

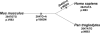
References
-
- Brooks-Wilson A, Marcil M, Clee SM, Zhang L, Roomp K, van Dam M, et al. Mutations in ABC1 in Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Nat Genet. 1999;22:336–345. - PubMed
-
- Bodzioch M, Orso E, Klucken J, Langmann T, Bottcher A, Diederich W, et al. The gene encoding ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 is mutated in Tangier disease. Nat Genet. 1999;22:347–351. - PubMed
-
- Rust S, Rosier M, Funke H, Amoura Z, Piette JC, Deleuze JF, et al. Tangier disease is caused by mutations in the gene encoding ATP-binding cassette transporter 1. Nat Genet. 1999;22:352–355. - PubMed
-
- Singaraja RR, Brunham LR, Visscher H, Kastelein JJ, Hayden MR. Efflux and atherosclerosis: The clinical and biochemical impact of variations in the ABCA1 gene. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:1322–1332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

