Splice variants of the NR1 subunit differentially induce NMDA receptor-dependent gene expression
- PMID: 16436592
- PMCID: PMC6674576
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3347-05.2006
Splice variants of the NR1 subunit differentially induce NMDA receptor-dependent gene expression
Abstract
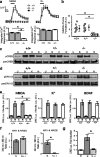
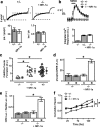
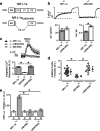
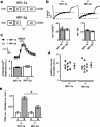
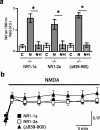
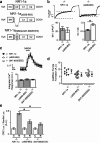
Subunits of the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) associate with many postsynaptic proteins that substantially broaden its signaling capacity. Although much work has been focused on the signaling of NR2 subunits, little is known about the role of the NR1 subunit. We set out to elucidate the role of the C terminus of the NR1 subunit in NMDAR signaling. By introducing a C-terminal deletion mutant of the NR1 subunit into cultured neurons from NR1(-/-) mice, we found that the C terminus was essential for NMDAR inactivation, downstream signaling, and gene expression, but not for global increases in intracellular Ca2+. Therefore, whereas NMDARs can increase Ca2+ throughout the neuron, NMDAR-dependent signaling, both local and long range, requires coupling through the NR1 C terminus. Two major NR1 splice variants differ by the presence or absence of a C-terminal domain, C1, which is determined by alternative splicing of exon 21. Analysis of these two variants showed that removal of this domain significantly reduced the efficacy of NMDAR-induced gene expression without affecting receptor inactivation. Thus, the NR1 C terminus couples to multiple downstream signaling pathways that can be modulated selectively by RNA splicing.
Figures

References
-
- Akyol Z, Bartos JA, Merrill MA, Faga LA, Jaren OR, Shea MA, Hell JW (2004). Apo-calmodulin binds with its C-terminal domain to the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NR1 C0 region. J Biol Chem 279:2166–2175. - PubMed
-
- Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S (2004). Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature 431:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME (1993). Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science 260:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ (1998). Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 21:13–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
