Transition from reversible to persistent binding of CaMKII to postsynaptic sites and NR2B
- PMID: 16436603
- PMCID: PMC2890238
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3116-05.2006
Transition from reversible to persistent binding of CaMKII to postsynaptic sites and NR2B
Abstract
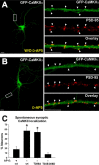
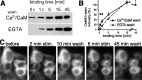
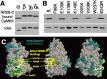
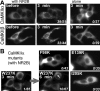
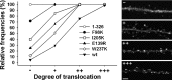
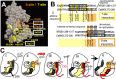
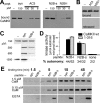
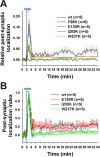
Changes in protein-protein interactions and activity states have been proposed to underlie persistent synaptic remodeling that is induced by transient stimuli. Here, we show an unusual stimulus-dependent transition from a short-lived to long-lasting binding between a synaptic receptor and its transducer. Both molecules, the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B and Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), are strongly implicated in mediating synaptic plasticity. We show that CaMKII reversibly translocates to synaptic sites in response to brief stimuli, but its resident time at the synapse increases after longer stimulation. Thus, CaMKII localization reflects temporal patterns of synaptic stimulation. We have identified two surface regions of CaMKII involved in short-lived and long-term interactions with NR2B. Our results support an initial reversible and Ca2+/CaM-dependent binding at the substrate-binding site ("S-site"). On longer stimulation, a persistent interaction is formed at the T286-binding site ("T-site"), thereby keeping the autoregulatory domain displaced and enabling Ca2+/CaM-independent kinase activity. Such dual modes of interaction were observed in vitro and in HEK cells. In hippocampal neurons, short-term stimulation initiates a reversible translocation, but an active history of stimulation beyond some threshold produces a persistent synaptic localization of CaMKII. This activity-dependent incorporation of CaMKII into postsynaptic sites may play a role in maturation and plasticity of synapses.
Figures

References
-
- Barria AS, Malinow R (2004). NMDA receptor subunits and synaptic plasticity. Soc Neurosci Abstr 30:55–20.
-
- Barria A, Malinow R (2005). NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron 48:289–301. - PubMed
-
- Bayer KU, Schulman H (2001). Regulation of signal transduction by protein targeting: the case for CaMKII. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:917–923. - PubMed
-
- Bayer KU, De Koninck P, Leonard AS, Hell JW, Schulman H (2001). Interaction with the NMDA receptor locks CaMKII in an active conformation. Nature 411:801–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
