Multiplexed detection of anthrax-related toxin genes
- PMID: 16436639
- PMCID: PMC1592686
- DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2006.050049
Multiplexed detection of anthrax-related toxin genes
Abstract
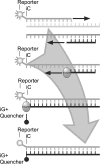
Simultaneous analysis of three targets in three colors on any real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) instrument would increase the flexibility of real-time PCR. For the detection of Bacillus strains that can cause inhalation anthrax-related illness, this ability would be valuable because two plasmids confer virulence, and internal positive controls are needed to monitor the testing in cases lacking target-specific signals. Using a real-time PCR platform called MultiCode-RTx, multiple assays were developed that specifically monitor the presence of Bacillus anthracis-specific virulence plasmid-associated genes. In particular for use on LightCycler-1, two triplex RTx systems demonstrated high sensitivity with limits of detection nearing single-copy levels for both plasmids. Specificity was established using a combination of Ct values and correct amplicon melting temperatures. All reactions were further verified by detection of an internal positive control. For these two triplex RTx assays, the analytical detection limit was one to nine plasmid copy equivalents, 100% analytical specificity with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 9%, and 100% analytical sensitivity with a CI of 2%. Although further testing using clinical or environmental samples will be required to assess diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, the RTx platform achieves similar results to those of probe-based real-time systems.
Figures


References
-
- Logan NA, Carman JA, Melling J, Berkeley RC. Identification of Bacillus anthracis by API tests. J Med Microbiol. 1985;20:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985;230:1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmaster AR, Ravel J, Rasko DA, Chapman GD, Chute MD, Marston CK, De BK, Sacchi CT, Fitzgerald C, Mayer LW, Maiden MC, Priest FG, Barker M, Jiang L, Cer RZ, Rilstone J, Peterson SN, Weyant RS, Galloway DR, Read TD, Popovic T, Fraser CM. Identification of anthrax toxin genes in a Bacillus cereus associated with an illness resembling inhalation anthrax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:8449–8454. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beyer W, Glockner P, Otto J, Bohm R. A nested PCR method for the detection of Bacillus anthracis in environmental samples collected from former tannery sites. Microbiol Res. 1995;150:179–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

