Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 16437532
- PMCID: PMC9006343
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005593
Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Since the introduction of the first cholinesterase inhibitor (ChEI) in 1997, most clinicians and probably most patients would consider the cholinergic drugs, donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine, to be the first line pharmacotherapy for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.The drugs have slightly different pharmacological properties, but they all work by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter associated with memory, by blocking the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. The most that these drugs could achieve is to modify the manifestations of Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane reviews of each ChEI for Alzheimer's disease have been completed (Birks 2005, Birks 2005b and Loy 2005). Despite the evidence from the clinical studies and the intervening clinical experience the debate on whether ChEIs are effective continues.
Objectives: To assess the effects of donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine in people with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.
Search strategy: The Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group's Specialized Register was searched using the terms 'donepezil', 'E2020' , 'Aricept' , galanthamin* galantamin* reminyl, rivastigmine, exelon, "ENA 713" and ENA-713 on 12 June 2005. This Register contains up-to-date records of all major health care databases and many ongoing trial databases.
Selection criteria: All unconfounded, blinded, randomized trials in which treatment with a ChEI was compared with placebo or another ChEI for patients with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.
Data collection and analysis: Data were extracted by one reviewer (JSB), pooled where appropriate and possible, and the pooled treatment effects, or the risks and benefits of treatment estimated.
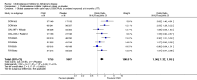
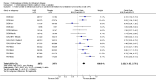
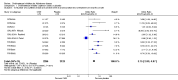
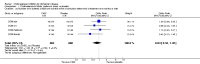
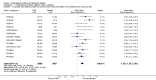
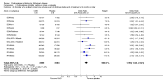
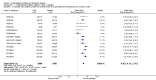
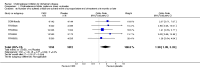
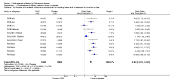
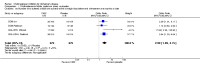
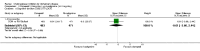
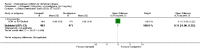
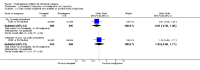
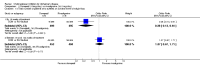
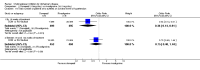
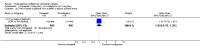
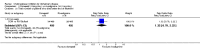
Main results: The results of 13 randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trials demonstrate that treatment for periods of 6 months and one year, with donepezil, galantamine or rivastigmine at the recommended dose for people with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease produced improvements in cognitive function, on average -2.7 points (95%CI -3.0 to -2.3), in the midrange of the 70 point ADAS-Cog Scale. Study clinicians blind to other measures rated global clinical state more positively in treated patients. Benefits of treatment were also seen on measures of activities of daily living and behaviour. None of these treatment effects are large. There is nothing to suggest the effects are less for patients with severe dementia or mild dementia, although there is very little evidence for other than mild to moderate dementia.More patients leave ChEI treatment groups, approximately 29 %, on account of adverse events than leave the placebo groups (18%). There is evidence of more adverse events in total in the patients treated with a ChEI than with placebo. Although many types of adverse event were reported, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, were significantly more frequent in the ChEI groups than in placebo. There are four studies, all supported by one of the pharmaceutical companies, in which two ChEIs were compared, two studies of donepezil compared with galantamine, and two of donepezil compared with rivastigmine. In three studies the patients were not blinded to treatment, only the fourth, DON vs RIV/Bullock is double blind. Two of the studies provide little evidence, they are of 12 weeks duration, which is barely long enough to complete the drug titration. There is no evidence from DON vs GAL/Wilcock of a treatment difference between donepezil and galantamine at 52 weeks for cognition, activities of daily living, the numbers who leave the trial before the end of treatment, the number who suffer any adverse event, or any specific adverse event. There is no evidence from DON vs RIV/Bullock of a difference between donepezil and rivastigmine for cognitive function, activities of daily living and behavioural disturbance at two years. Fewer patients suffer adverse events on donepezil than rivastigmine.
Authors' conclusions: The three cholinesterase inhibitors are efficacious for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. It is not possible to identify those who will respond to treatment prior to treatment. There is no evidence that treatment with a ChEI is not cost effective. Despite the slight variations in the mode of action of the three cholinesterase inhibitors there is no evidence of any differences between them with respect to efficacy. There appears to be less adverse effects associated with donepezil compared with rivastigmine. It may be that galantamine and rivastigmine match donepezil in tolerability if a careful and gradual titration routine over more than three months is used. Titration with donepezil is more straightforward and the lower dose may be worth consideration.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

























































References
References to studies included in this review
DON‐302 {published data only}
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Gordon B, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD, Donepezil Study Group. Open‐label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 2001;58(3):427‐33. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H. Gauthier S. Hecker J. Vellas B. Subbiah P. Whalen E. Donepezil MSAD Study Investigators Group. Erratum: a 24‐week, randomized, double‐blind study of donepezil in moderate to severe alzheimer's disease. Neurology 2001; Vol. 57, issue 11:2153. - PubMed
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers L. Donepezil lengthens time to loss of activities of daily living in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease ‐ results of a preliminary evaluation. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. Boston. Neurology 1997;48(3):A100.
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers SL. Donepezil lengthens time to loss of activities of daily living and cognition in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13‐17, Vienna, Austria 1997. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers SL. Donepezil maintains activities of daily living in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease: results of a retrospective analysis. Eur J Neurology 1997;4, Suppl 1:S9.
DON‐304 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bayer AJ, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Burns A, Petite H, Moller HJ, Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT, International Donepezil Study Group. Donepezil improves functional activity in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 21st Collegium Internationale Neuro psychopharmacologicum; 1998 Jul 12‐16, Glasgow, Scotland 1998. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Burns A, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Petit H, Möller H‐J, Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT and the International Donepezil Study Group. The effects of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease ‐ results from a multinational trial. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 1999;10(3):237‐244. - PubMed
-
- Gauthier S, Rosser M, Hecker J, Petite H, Rogers S, Mohr E, Burns A, Friedhoff LT, Rogers S. Donepezil Produces Both Clinical Global and Cognitive Test Improvement in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease. Proceedings of the 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1998 May 30‐Jun 4, Toronto, Canada 1998b. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Gauthier S, Rossor M, Hecker J, et al. Results from a multinational Phase III clinical trial of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease. [abstract] [poster presentation at 5th International Geneva/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer therapy] April 15‐18 1998.
-
- Pratt RD, Gauthier S, Burns A, Perdomo CA. Donepezil provides long‐term clinical benefits for patients with Alzheimers Disease. Proceedings of the World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 Jul 9‐13, Washington 2000a.
DON‐311 {published data only}
-
- Finucane TE, Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, Whalen E. Getting donepezil into the nursing home. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003; Vol. 51, issue 1:133‐134. - PubMed
-
- Steinman MA, Covinsky KE, Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, Whalen E. Donepezil for nursing home patients with dementia: a reinterpretation of the evidence. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting J Am Geriatr Soc 2001;49:1590‐9.. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(1):132‐133. - PubMed
-
- Tariot P, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Perdomo CA, Whalen E, Sovel MA, Schwam EM. Donepezil was well‐tolerated and enhanced cognition in nursing home patients with alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1999; Vol. 47:S3. - PubMed
-
- Tariot P, Perdomo CA, Whalen E, Sovel MA, Scham EM. Age is not a barrier to donepezil treatment of Alzheimer's disease in the long‐term care setting. International Psychogeriatrics. 1999; Vol. 11, issue Supplement 1:134.
-
- Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, Whalen E. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of Donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001; Vol. 49, issue 12:1590‐9. - PubMed
DON‐402 {published data only}
-
- Seltzer B, Zolnouni P, Nunez M, Goldman R, Kumar D, Ieni J, Richardson S, Donepezil 402 Study Group. Efficacy of donepezil in early‐stage Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurolology 2004;61:1852‐6. - PubMed
DON‐Feldman {published data only}
-
- Feldman H. Therapeutic benefits of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor therapy in the moderate to severe stage of alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; 2000 Apr 5‐8, Stockholm 2000:59.
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Hux M, Emir B, Subbiah P, Mastery V. Improved health outcomes with donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease are associated with economic benefits. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:285.
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Emir B, Mastey V, Subbiah P, and the Donepezil Study Group. Efficacy of donepezil on maintenance of activities of daily living in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease and the effect on caregiver burden. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51:737‐744. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Hux M, Xu Y, Schwam EM, Shah S, Mastey V, Donepezil MSAD Study Investigators Group. Economic evaluation of donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2004;63(4):644‐650. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Ieni J, Xu Y, Schwam E. Treatment Benefits of Donepezil in Patients with Severe Alzheimer's Disease and Their Caregivers. 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005 2005b:P02.097. 2005.
DON‐Nordic {published data only}
-
- Engedal K, Soininen H, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Winblad B, Wimo A, Wetterholm AL, Zhang R, Haglund A, Subbiah P. Donepezil improved or stabilized cognition over one year in patients with mild and moderate alzheimer's disease. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(Suppl 3):S368.
-
- Mastey V, Wimo A, Winblad B, Haglund A, Jacobson L, Miceli R, Zhang R, Subbiah P. An economic evaluation of donepezil in mild to moderate alzheimer's disease: results of a one year, double‐blind, randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001;49(4):S131.
-
- Mastey V, Wimo A, Winblad B, Haglund A, Jacobson L, Miceli R, Zhang R, Subbiah P. Donepezil reduces the time caregivers spend providing care: results of a one‐year, double‐blind, randomized trial in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 Feb 23‐26, San Francisco 2001.
-
- Soininen H, Winblad B, Engedal K, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Wimo A, Wetterholme AL, Zhang R, Hugland A, Subbiah P. Long term benefits of donepezil on ADLs in AD patients. Proceedings of the Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Geriatric Society and the American Federation for Aging Research; 2000 May 17‐21, Nashville. 2000:171.
-
- Soininen H, Winblad B, Engedal K, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Wimo A, Zhang R, Subbiah P, Donepezil Nordic Study Group. Response to Donepezil is not predicted by apolipoprotein E genotype and/or gender. Proceedings of the World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 Jul 9‐13, Washington 2000.
DON vs RIV/Bullock {published data only}
-
- Bullock R, Touchon J, Bergman H, Gambina G, He Y, Rapatz G, Nagel J, Lane R. Rivastigmine and donepezil treatment in moderate to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease over a 2‐year period. Current Medical Research and Opinions 2005;21(8):1317‐1327. - PubMed
GAL‐INT‐1 Wilcock {published data only}
-
- Wilcock GK. Erratum: Efficacy and safety of galantamine in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: Multicentre randomised controlled trial (British Medical Journal (December 9)(1445‐1449)). BR‐MED‐J: British‐Medical‐Journal 2001;322(7278):90.
-
- Wilcock GK. GALANTAMINE ALLEVIATES CAREGIVER BURDEN IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE: A 6‐MONTH PLACEBO‐CONTROLLED STUDY. Conference Proceedings World Alzheimer Congress; 9‐13 July, 2000, Washington. 2000.
GAL‐USA‐10 Tariot {published data only}
-
- Tariot PN, Solomon PR, Morris JC, Kershaw P, Lilienfeld S, Ding C, Galantamine USA‐10 Study Group. A 5‐month, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of galamtine in AD. Neurology 2000;54(12):2269‐2276. - PubMed
GAL‐USA‐1 Raskind {published data only}
-
- Raskind MA, Peskind ER, Wessel T, Yuan W, Galantamine USA‐1 Study Group. Galantamine in AD: A 6‐month randomized placebo‐controlled trial with a 6‐month extension. Neurology 2000;54(12):2261‐2268. - PubMed
RIV‐B303 {published data only}
-
- Anand R, Hartman R, Graham S. Effects dof Alzheimer's disease severity on activities of daily living with long‐term rivastigmine treatment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001;49(4):S151.
-
- Anand R, Messina J, Veach J, Hartman R. Effects of Rivastigmine in patients with moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; April 5‐8, 2000; Stockholm, Sweden. 2000:199.
-
- Farlow M, Anand R, Messina J, Hartman R. Increased cognitive efficacy of rivastigmine in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease with co‐existing vascular risk. Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; April 5‐8, 2000; Stockholm, Sweden. 2000:206.
-
- Farlow M, Messina J, Anand R, Hartman R, Veach J. Dose dependent effect of rivastigmine on progression of cognitive deterioration in Alzheimer's disease. In: Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; April 5‐8, 2000; Stockholm, Sweden. 2000. 2000:172.
-
- Hebert M. [Alzheimer disease: efficacy and tolerance of rivastigmine] [Maladie d'Alzheimer: efficacite et tolerance de la rivastigmine]. Presse Medicale 1999;28(32):1757‐8. - PubMed
RIV‐B304 {published data only}
-
- Lindesay J. An open label one‐year extension of SDZ‐ENA‐713 studies B303, B304 and B305 to prospectively evaluate long‐term safety, tolerability and efficacy of SDZ‐ENA‐713 in out‐patients with probable Alzheimer's disease. National Research Register 2000.
-
- Novartis. No title. Unpublished. Data provided by Novartis No year.
-
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. ADENA Programme. Unpublished Data 1998.
RIV‐B351 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. No title. Unpublished. Data provided by Novartis No year.
-
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. ADENA Programme. Unpublished Data 1998.
RIV‐B352 {published data only}
-
- Corey‐Bloom J, Anand R and Veach J for ENA 713 B352 Study Group. A randomized trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of ENA 713 (rivastigmine tartrate), a new acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. Int J Ger Psychopharmacology 1998;1:55‐65.
-
- Doraiswamy M. The effects of rivastigmine on the alzheimer's disease assessment scale‐cognitive subscale items scores of patients with alzheimer's disease. Health in aging the challenge and promise of new decade. Proceedings of the annual scientific meeting of the American geriatrics society and the American federation for aging research; 2000 May 17‐21, Nashville. 2000:173.
-
- Doraiswamy PM, Anand R, Hartman R. Cognitive effects of rivastigmine in patients with mild to moderate alzheimer's disease compared to those with moderately‐severe to severe AD. Clinical Neuropschological Assessment 2000;1(6):12.
-
- Doraiswamy PM, Anand R, Hartman R. Long term cognitive effects in Alzheimer's disease patients stratified by vascular risk score and treated for 1 year with rivastigmine. Clinical Neuropschological Assessment 2000;1(6):14.
-
- Farlow M, Hake A, Messina J, Veach J, Anand R. The response of patients with Alzheimer's disease to rivastigmine treatment is predicted by the rate of disease progression. Neurology 2000; Vol. 54, issue Suppl 3:A469. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
AD2000 {published data only}
-
- AD2000 Collaborative Group. Long‐term donepezil treatment in 565 patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD2000): randomised double‐blind trial. Lancet 2004;363:2105‐15. - PubMed
-
- Bentham P, Gray R, Hill R, Sellwood E, Courtney C. Twelve week respone to cholinesterase inhibitors dose not predict future benefit the AD2000 trial experiance. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:337.
-
- Lendon CL. Determination of respones to anticholinesterase therapy in the treatment of Alzheimer's disaese. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:1287.
-
- Lendon CL. Determination of responses to anticholinesterase therapy in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders; 2002 July 20‐25, Stockholm, Sweden: Abstract No 1287. 2002.
-
- Roberts N. A reliable assessment of the efficacy and safety of donepezil and aspirin in Alzheimer's disease (AD2000). National Research Register 2001.
Donepezil‐203 {published data only}
-
- Tune L, Tiseo P, Hoffman J, Perdomo C, Votaw J, Rogers S, Friedhoff L. PET in AD: Donepezil HCl (E2020) maintains functional brain activity in patients with Alzheimer's disease: results of a 24‐week study. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 Feb 23‐26 San Francisco. 2001.
-
- Tune L, Tiseo PJ, Ieni J, Perdomo C, Pratt RD, Votaw JR, Jewart RD, Hoffman JM. Donepezil HCl (E2020) maintains functional brain activity in patients with Alzheimer disease: results of a 24‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;11(2):169‐177. - PubMed
-
- Tune LE, Tiseo PJ, Hoffman JM, Perdomo CA, Votow JR, Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Functional Brain Activity in Alzheimer's Disease. Proceedings of the 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1998 May 30‐ Jun 4, Toronto. 1998:NR345. [MEDLINE: ]
Donepezil‐204 {published data only}
-
- Anon. No title. Eisai Inc..
DON vs GAL/Jones {published data only}
-
- Jones RW, Soininen H, Hager K, Aarsland D, Passmore P, The DONGAL Study Group, Murthy A, Zhang R, Bahra R. A multinational, randomised, 12‐week study comparing the effects of donepezil and galantamine in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19:58‐67. - PubMed
DON vs GAL/Wilcock {published data only}
-
- Wilcock G, Howe I, Coles H, Lilienfeld S, Truyen L, Young Z, Bullock R, and members of the GAL‐GBR‐2 Study Group. A long‐term comparison of galantamine and donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Drugs Aging 2003;20(10):777‐789. - PubMed
DON vs RIV/Wilkinson {published data only}
-
- Bullock R, Passmore F, Potocnik F, Hock C. The tolerability, ease of use and efficacy of donepezil and rivastigmine in alzeimer's disease patients: a 12‐week, multinational, comparative study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001; Vol. 49, issue 4:S19.
-
- Bullock R, Wilkinson DG, Passmore P, Hopker SW, Smith R, Potocnik FC, Maud CM, Hock C. Caregiver and physician determination of satisfaction with and ease of use of donepezil and rivastigamine treatment in alzheimer's disease patients. Proceedings of the 17th Alzheimer's Disease International Conference; 2001 Oct 25‐27, Christchurch, New Zealand 2001:39.
-
- Böttcher‐Buhler E. [Well tolerated, effective and inexpensive therapy of Alzheimer's dementia with donepezil] [Therapie der Alzheimer‐Demenz mit Donepezil: gut vertraglich, wirksam und kostengunstig]. Neurologie und Rehabilitation 2000; Vol. 6, issue 6:332‐3.
-
- Potocnik FC, Smith R, Passmore P, Hock C, Wilkinson D, Maud CM, Hopker S. Tolerability, ease of use, and efficacy of donepezil and rivastigmine in alzheimer's disease patients. Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; New Orleans 2001.
-
- Wilkinson D, Passmore P, Potocnik F, Maud C, Hock C. Donepezil compared to rivastigmine in Alzheimer's disease: similar efficacy but better tolerability and physician and caregiver satisfaction in a multinational randomized trial. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 Feb 23‐26, San Francisco 2001.
Fuschillo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fuschillo C, Pia S, Campana F, Pinto A, Simone L. Cognitive deficits in alzheimer's disease: treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitor agents. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2001;33(Suppl 1):151‐8. - PubMed
GAL‐INT‐10 {published data only}
-
- Brodaty H, Corey‐Bloom J, Potocnik FCV, Truyen L, Gold M, Damaraju CRV. Galantamine Prolonged‐Release Formulation in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2005;20(2‐3):120‐132. - PubMed
GAL‐INT‐6Erkinjuntti {published data only}
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Kurz A, Gauthier S, Bullock R, Lilienfeld S, Damaraju CV. Efficacy of galantamine in probable vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease combined with cerebrovascular disease: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002;359:1283‐1290.. - PubMed
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Kurz A, Gauthier S, Bullock R, Lilienfeld S, Damaraju CV. The safety and efficacy of Galantamine in the treatment of vascular and mixed dementia (Double‐blind part only). (GAL‐INT‐6). Johnson and Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development. January 2004.
Krishnan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Krishnan KR, Charles HC, Doraiswamy PM, Mintzer J, Weisler R, Yu X, Perdomo C, Ieni JR, Rogers S. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of the effects of donepezil on neuronal markers and hippocampal volumes in Alzheimer's disease. American journal of psychiatry, The 2003;160(11):2003‐11. - PubMed
Mega 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mega M, Dinov I, Manese M, Felix J, O'Connor S, Toga A, Cummings J. Cerebral metabolic activation with cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer's disease. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:430.
Rozzini 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rozzini L, Bargnani C, Bosio A, Chia F, Franzani S, Leonardi R, Ranzenigo A, Rozzini R, Saviotti FM, Turla M, Trabucchi m, Ghianda D, Borroni B, Chilovi BV, Padovani A. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are effective in real world patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease evidence from a large population treated with rivastigmine or donepezil. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:329.
-
- Rozzini L, Bargnani C, Bosio A, Chia F, Franzoni S, Leonardi R, Ranzenigo A, Rozzini R, Saviotti FM, Turla M, Trabucchi M, Vicini B, Borroni B, Padovani A. Comparison of efficacy and safety of rivastigmine and donepezil in patients with mild to moderate alzheimer disease: results from a multicentre randomised trial.. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:240.
Shua‐Haim 2002b {published data only}
-
- Shua‐Haim J, Smith J, Potel S. A head to study of donepezitl aricept rivastigmine exlon and galantamine reminyl for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease safety tolerability clinical and caregiver impression after 4‐5 months of trratment a prospective study. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:286.
Study 312/314 {published data only}
-
- Ebell M. Does donepezil help patients with moderate Alzheimer's dementia preserve their ability to function independently?. Evidence Based Practice 2002.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni J, Perdomo C, Pratt R, Rogers S. Donepezil preserves activities of daily living in alzheimer's disease patients: results from a one‐year placebo‐controlled functional survival study. Neurology 2000; Vol. 54, issue Suppl 3:A415.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni J, Rogers S, Perdomo C, Pratt R. Donepezil preserves functional status and improves cognition in alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year propective placebo‐controlled study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000; Vol. 48, issue 8:S46.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni JR, Rogers SL, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD. Donepezil preserves functional status in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year prospective placebo‐controlled attrition study. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9(Suppl 5):S328.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni JR, Rogers SL, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD. Donepezil preserves functional status in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year prospective placebo‐controlled study. Proceedings of the Quality Research in Dementia Conference; 2000 Nov 19‐22, London. 2000.
Tsolaki 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tsolaki M, Gerothanassis D, Aristotle CP. Efficacy and safety of cholinesterase inhibitors a longitudinal comparative study between donepezil and rivastigmine. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:2038.
Wang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Chen Q, Zhang Z, et al. The treatment by using rivastigmine for patients with alzheimer disease: results of a multicenter, randomized, open‐labeled, controlled clinical trial. Chinese Journal of Neurology 2001;34(4):210‐3.
Werber 2002 {published data only}
-
- Werber EA, Klein C, Rabey MJ. Evaluation of cholinergic treatment in demented by p300 evoked related potentials. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:442.
Additional references
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington DC: APA, 1987:American Psychiatric Association.
Birks 2005
-
- Birks JS, Harvey R. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library 2005, Issue 3. - PubMed
Birks 2005b
-
- Birks J, Grimley Evans J, iakovidou V, Tsolaki M. Rivastigmine for Alzheimer's disease (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library 2005, Issue 3. - PubMed
Bucks 1996
-
- Bucks RS, Ashworth DL, Wilcock GK, Siegfried K. Assessment of activities of daily living in dementia: development of the Bristol activities of daily living scale. Age Ageing 1996;25:113‐120. - PubMed
Cummings 1994
-
- Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenburg‐Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J. The neuropsychiatric Inventory: Comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994;44:2308‐2313. - PubMed
DeJong 1989
-
- DeJong R, Osterlund OW, Roy GW. Measurement of quality‐of‐life changes in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Clin Ther 1989;11(4):545‐554. - PubMed
Erkinjuntti 2002
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Skoog I, Lane R, Andrews C. Rivastigmine in patients with Alzheimer's disease and concurrent hypertension. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2002;56(10):791‐796. - PubMed
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein NF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 1975;12:189‐198. - PubMed
Galasko 1997
-
- Galasko D, Bennett D, Sano M, et al. An inventory to assess activities of daily living for clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. The Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 1997;11(Suppl 2):533‐539. - PubMed
Gottfries 1982
-
- Gottfries CG, Brane G, Gullberg B, Steen G. A new rating scale for dementia syndromes. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 1982;1:311‐330. - PubMed
Gélinas 1999
-
- Gélinas I, Gauthier L, McIntyre M, et al. Development of a functional measure for persons with Alzheimer's disease: the Disability Assessment for Dementia. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1999;53:471‐481. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Kumar 2000
-
- Kumar V, Anand R, Messina J, Hartman R, Veach J. An efficacy and safety analysis of Exelon in Alzheimer's disease patients with concurrent vascular risk factors. European Journal of Neurology 2000;7(2):159‐169. - PubMed
Loy 2005
-
- Loy C, Schneider L. Galantamine for Alzheimer's disease (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library 2005, Issue 3. - PubMed
McKhann 1987
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;4:939‐944. - PubMed
Olin 2005
-
- Olin J, Schneider L. Galantamine for Alzheimer's disease (Cochrane Library). The Cochrane Library 2005, Issue 3.
Panisset 1994
-
- Panisset M, Roudier M, Saxton J, Boller F. Severe impairment battery. A neurological test for severely demented patients. Archives of Neurology 1994;51:41‐45. - PubMed
Reisberg 1982
-
- Reisberg B, Ferris SH, Leon MJ, Crook T. the global deterioration sclae for assessment of primary degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry 1982;139:1136‐1139. - PubMed
Rosen 1984
-
- Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis K. A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease. Am J Psychiatry 1984;141:1356‐1364. - PubMed
Schneider 1997
-
- Schneider LS, Olin JT, Doody RS, et al. Validity and reliability of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study ‐ Clinical Global Impression of Change. AD Assoc Dis 1997;11(suppl 2):S22‐32. - PubMed
Wimo 1998
-
- Wimo A, Wetterholm AL, Mastey V, Winblad B. Evaluation of the healthcare resource utilization and caregiver time in anti‐dementia drug trials. In: Wimo A, Jönsson B, Karlsson G, Winblad B editor(s). Health Economics in Dementia. Chichester: Wiley, 1998:465‐477.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

