Effect of synbiotics on intestinal microflora and digestive enzyme activities in rats
- PMID: 16437710
- PMCID: PMC4725162
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i47.7413
Effect of synbiotics on intestinal microflora and digestive enzyme activities in rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of synbiotics, i.e. probiotics and prebiotics mixture, on the gut microbial ecology and digestive enzyme activities in rats.
Methods: Forty-eight SD rats weighing about 280 g were used in this study. Rats were divided into three groups according to the contents of probiotics and prebiotics mixture in the feed as control, low and high dose groups. The duration of the experiment was 8 wk.
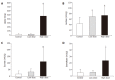
Results: Compared with the control group, the fecal Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium counts were significantly increased and the fecal Coliform organism counts were markedly reduced in the low and high dose groups. Concerning the digestive enzyme activity of jejunum, only lactase activity increased in low dose group. However, significant increase of lipase, lactase, sucrase, and isomaltase activities were observed in high dose group.
Conclusion: Intake of low and high dosages of probiotics and prebiotics mixture significantly improved the ecosystem of the intestinal tract by increasing the probiotics population and digestive enzyme activities in rats.
Figures

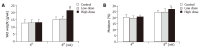
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of probiotics on intestinal barrier function in malnourished rats after liver transplantation.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011 Oct;10(5):489-96. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(11)60083-0. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011. PMID: 21947722
-
Relationship between dietary-induced changes in intestinal commensal microflora and duodenojejunal myoelectric activity monitored by radiotelemetry in the rat in vivo.Exp Physiol. 2006 Jan;91(1):229-37. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031708. Epub 2005 Nov 1. Exp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16263800
-
Effect on components of the intestinal microflora and plasma neuropeptide levels of feeding Lactobacillus delbrueckii, Bifidobacterium lactis, and inulin to adult and elderly rats.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Oct;72(10):6533-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00915-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17021202 Free PMC article.
-
[Dysbacteriosis and preparations with probiotic function].Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2004 Jan-Feb;(1):84-92. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2004. PMID: 15024992 Review. Russian.
-
Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity.Nutr Res Rev. 2018 Jun;31(1):35-51. doi: 10.1017/S095442241700018X. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Nutr Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29037268 Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: Safe options for next-generation therapeutics.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;106(2):505-521. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11646-8. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35015145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prebiotics in chronic intestinal inflammation.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009 Mar;15(3):454-62. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20737. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. PMID: 18831524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of intestinal microbiota and enzyme activities in mice fed with lily bulb.3 Biotech. 2021 Jan;11(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02597-4. Epub 2021 Jan 2. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33442516 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the prebiotic effect of raw and roasted almonds (Prunus amygdalus).J Sci Food Agric. 2016 Mar 30;96(5):1836-43. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7604. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Sci Food Agric. 2016. PMID: 26749248 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of indigenous oxalate degrading lactic acid bacteria from human faeces and South Indian fermented foods: assessment of probiotic potential.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Feb 11;2014:648059. doi: 10.1155/2014/648059. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24723820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Djouzi Z, Andrieux C, Degivry MC, Bouley C, Szylit O. The association of yogurt starters with Lactobacillus casei DN 114.001 in fermented milk alters the composition and metabolism of intestinal microflora in germ-free rats and in human flora-associated rats. J Nutr. 1997;127:2260–2266. - PubMed
-
- Collins MD, Gibson GR. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: approaches for modulating the microbial ecology of the gut. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69:1052S–1057S. - PubMed
-
- Cui HH, Chen CL, Wang JD, Yang YJ, Sun Y, Wang YD, Lai ZS. The effects of bifidobacterium on the intestinal mucosa of the patients with ulcerative colitis. Zhonghua NeiKe ZaZhi. 2003;42:554–557. - PubMed
-
- Duffy LC, Zielezny MA, Riepenhoff-Talty M, Dryja D, Sayahtaheri-Altaie S, Griffiths E, Ruffin D, Barrett H, Rossman J, Ogra PL. Effectiveness of Bifidobacterium bifidum in mediating the clinical course of murine rotavirus diarrhea. Pediatr Res. 1994;35:690–695. - PubMed
-
- Yolken RH, Ojeh C, Khatri IA, Sajjan U, Forstner JF. Intestinal mucins inhibit rotavirus replication in an oligosaccharide-dependent manner. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:1002–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

