Two internal ribosome entry sites mediate the translation of p53 isoforms
- PMID: 16440000
- PMCID: PMC1456917
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400623
Two internal ribosome entry sites mediate the translation of p53 isoforms
Abstract
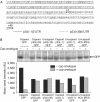
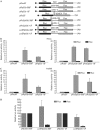
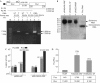
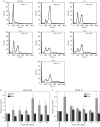
The p53 tumour suppressor protein has a crucial role in cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Previous reports show that the p53 messenger RNA is translated to produce an amino-terminal-deleted isoform (DeltaN-p53) from an internal initiation codon, which acts as a dominant-negative inhibitor of full-length p53. Here, we show that two internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) mediate the translation of both full-length and DeltaN-p53 isoforms. The IRES directing the translation of full-length p53 is in the 5'-untranslated region of the mRNA, whereas the IRES mediating the translation of DeltaN-p53 extends into the protein-coding region. The two IRESs show distinct cell-cycle phase-dependent activity, with the IRES for full-length p53 being active at the G2-M transition and the IRES for DeltaN-p53 showing highest activity at the G1-S transition. These results indicate a novel translational control of p53 gene expression and activity.
Figures
References
-
- Barraille P, Chinestra P, Bayard F, Faye JC (1999) Alternative initiation of translation accounts for a 67/45 kDa dimorphism of the human estrogen receptor ERα. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 84–88 - PubMed
-
- Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1998) Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 282: 1497–1501 - PubMed
-
- Cornelis S, Bruynooghe Y, Denecker G, Van Huffel S, Tinton S, Beyaert R (2000) Identification and characterization of a novel cell cycle-regulated internal ribosome entry site. Mol Cell 5: 597–605 - PubMed
-
- Courtois S, Verhaegh G, North S, Luciani MG, Lassus P, Hibner U, Oren M, Hainaut P (2002) N-p53, a natural isoform of p53 lacking the first transactivation domain, counteracts growth suppression by wild-type p53. Oncogene 21: 6722–6728 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

