Granzyme A, which causes single-stranded DNA damage, targets the double-strand break repair protein Ku70
- PMID: 16440001
- PMCID: PMC1456912
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400622
Granzyme A, which causes single-stranded DNA damage, targets the double-strand break repair protein Ku70
Abstract
Granzyme A (GzmA) induces caspase-independent cell death with morphological features of apoptosis. Here, we show that GzmA at nanomolar concentrations cleaves Ku70, a key double-strand break repair (DSBR) protein, in target cells. Ku70 is cut after Arg(301), disrupting Ku complex binding to DNA. Cleaving Ku70 facilitates GzmA-mediated cell death, as silencing Ku70 by RNA interference increases DNA damage and cell death by GzmB cluster-deficient cytotoxic T lymphocytes or by GzmA and perforin, whereas Ku70 overexpression has the opposite effect. Ku70 has two known antiapoptotic effects-facilitating DSBR and sequestering bax to prevent its translocation to mitochondria. However, GzmA triggers single-stranded, not double-stranded, DNA damage, and GzmA-induced cell death does not involve bax. Therefore, Ku70 has other antiapoptotic functions in GzmA-induced cell death, which are blocked when GzmA proteolyses Ku70.
Figures

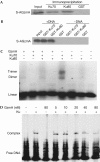



References
-
- Andrade F, Roy S, Nicholson D, Thornberry N, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L (1998) Granzyme B directly and efficiently cleaves several downstream caspase substrates: implications for CTL-induced apoptosis. Immunity 8: 451–460 - PubMed
-
- Bell JK, Goetz DH, Mahrus S, Harris JL, Fletterick RJ, Craik CS (2003) The oligomeric structure of human granzyme A is a determinant of its extended substrate specificity. Nat Struct Biol 10: 527–534 - PubMed
-
- Beresford PJ, Xia Z, Greenberg AH, Lieberman J (1999) Granzyme A loading induces rapid cytolysis and a novel form of DNA damage independently of caspase activation. Immunity 10: 585–594 - PubMed
-
- Beresford PJ, Zhang D, Oh DY, Fan Z, Greer EL, Russo ML, Jaju M, Lieberman J (2001) Granzyme A activates an endoplasmic reticulum-associated caspase-independent nuclease to induce single-stranded DNA nicks. J Biol Chem 276: 43285–43293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

