Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative TNM staging of gastric cancer
- PMID: 16440415
- PMCID: PMC4077489
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i1.43
Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative TNM staging of gastric cancer
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the value of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in the preoperative TNM staging of gastric cancer.
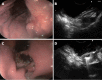
Methods: Forty-one patients with gastric cancer (12 early stage and 29 advanced stage) proved by esophagogastroduodenoscopy and biopsies preoperatively evaluated with EUS according to TNM (1997) classification of International Union Contrele Cancer (UICC). Pentax EG-3630U/Hitachi EUB-525 echo endoscope with real-time ultrasound imaging linear scanning transducers (7.5 and 5.0 MHz) and Doppler information was used in the current study. EUS staging procedures for tumor depth of invasion (T stage) were performed according to the widely accepted five-layer structure of the gastric wall. All patients underwent surgery. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS for TNM staging of gastric cancer was determined by comparing preoperative EUS with subsequent postoperative histopathologic findings.
Results: The overall diagnostic accuracy of EUS in preoperative determination of cancer depth of invasion was 68.3% (41/28) and 83.3% (12/10), 60% (20/12), 100% (5/5), 25% (4/1) for T1, T2, T3, and T4, respectively. The rates for overstaging and understaging were 24.4% (41/10), and 7.3% (41/3), respectively. EUS tended to overstage T criteria, and main reasons for overstaging were thickening of the gastric wall due to perifocal inflammatory change, and absence of serosal layer in certain areas of the stomach. The diagnostic accuracy of metastatic lymph node involvement or N staging of EUS was 100% (17/17) for N0 and 41.7% (24/10) for N+, respectively, and 66% (41/27) overall. Misdiagnosing of the metastatic lymph nodes was related to the difficulty of distinguishing inflammatory lymph nodes from malignant lymph nodes, which imitate similar echo features. Predominant location and distribution of tumors in the stomach were in the antrum (20 patients), and the lesser curvature (17 patients), respectively. Three cases were found as surgically unresectable (T4 N+), and included as being correctly diagnosed by EUS.
Conclusion: EUS is a useful diagnostic method for preoperative staging of gastric cancer for T and N criteria. However, EUS evaluation of malignant lymph nodes is still unsatisfactory.
Figures

References
-
- Mehta VK, Fisher G. Gastric cancer. Accessed 2004-11-03. Available from: http: //www.emedicine.com/med/topic845.htm.
-
- Neugut AI, Hayek M, Howe G. Epidemiology of gastric cancer. Semin Oncol. 1996;23:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Chak A. EUS in submucosal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:S43–S48. - PubMed
-
- Rösch T, Kapfer B, Will U, Baronius W, Strobel M, Lorenz R, Ulm K. Accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography in upper gastrointestinal submucosal lesions: a prospective multicenter study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:856–862. - PubMed
-
- Chak A, Canto MI, Rosch T, Dittler HJ, Hawes RH, Tio TL, Lightdale CJ, Boyce HW, Scheiman J, Carpenter SL, et al. Endosonographic differentiation of benign and malignant stromal cell tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;45:468–473. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

